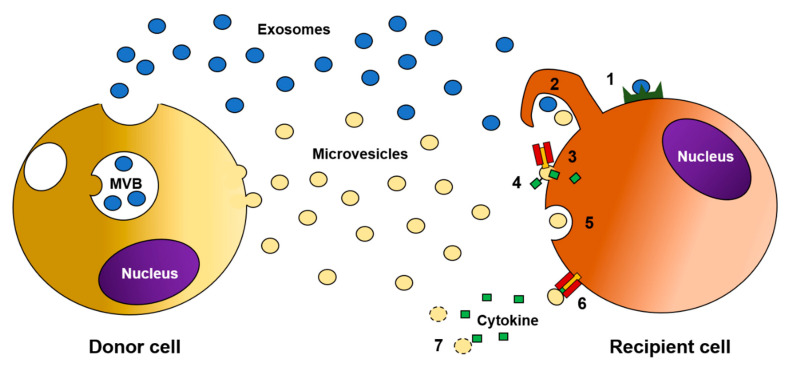
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of cytokine delivery via extracellular release and uptake. Following extracellular vesicle (EV) release, through their respective biogenesis pathways, EVs can facilitate the intracellular delivery of cytokines into recipient cells by clathrin-mediated endocytosis (1), macropinocytosis (2), cell membrane fusion (3), and phagocytosis (4). EV membrane fusion also allows the lateral transfer of EV-tethered cytokines and cytokine receptors to the surface of recipient cells (5). Additionally, EV-tethered cytokines can directly interact with their cognate cell surface receptors on target cells (6). Finally, cytokines can be released from EV encapsulation and directly into the extracellular space whereby the cytokines in question can exert their effect (7) [60].