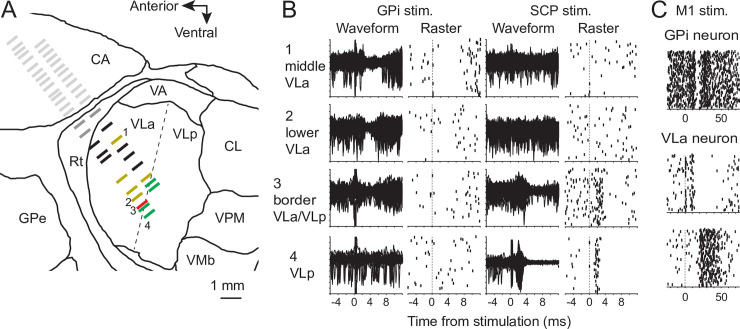
Fig 1.
(A-B) Exemplar results from microelectrode mapping in the vicinity of the VLa thalamus. Single units encountered along parallel electrode trajectories were classified as being located in striatum (light gray tick marks), Rt (dark gray), or the VL thalamus. Neurons in VL thalamus were further classified as VLa neurons if they were inhibited by stimulation (“stim.”) of the GPi and not excited by stimulation of SCP (yellow tick marks). Fig 1B1-2 shows overlaid peri-stimulus raw waveforms (left) and raster plots of sorted spikes (right) from two example locations in VLa (locations 1 and 2 in Fig 1A and 1B) at which GPi stimulation evoked a pause in neuronal activity and SCP stimulation had no effect. Neurons in VL were classified as VLp neurons if they were excited by stimulation of SCP and did not respond to stimulation of the GPi (green tick marks in Fig 1A; e.g., location 4 in Fig 1A and 1B). Neurons located at the border between VLa and VLp occasionally responded to stimulation of both GPi and SCP (red tick mark, location 3 in Fig 1A and 1B). Neurons that did not respond to stimulation were classified as VLa neurons (black tick marks Fig 1A) only if they were located antero-dorsal to the VLa/VLp boundary and postero-ventral to the Rt. (C) Regions of the GPi and VLa that belong to the arm-related BG-thalamic circuit were identified by testing for short-latency effects of electrical stimulation in arm-related areas of primary motor cortex. GPi neurons were included if sampled from regions at which stimulation of motor cortex (time zero) evoked a triphasic response at short latency (top, raster plot of sorted spikes). VLa neurons were included if sampled from regions at which stimulation of motor cortex evoked a pause or burst of activity at short latency (middle and bottom panels, respectively). BG, basal ganglia; CA, caudate; GPe, globus pallidus-externa; GPi, globus pallidus-internus; Rt, reticular nucleus of the thalamus; SCP, superior cerebellar peduncle; VA, ventral anterior nucleus; VLa, ventrolateral anterior nucleus; VLp, ventrolateral posterior nucleus; VMb, ventral medial-basal nucleus; VPM, ventral posterior-medial nucleus.