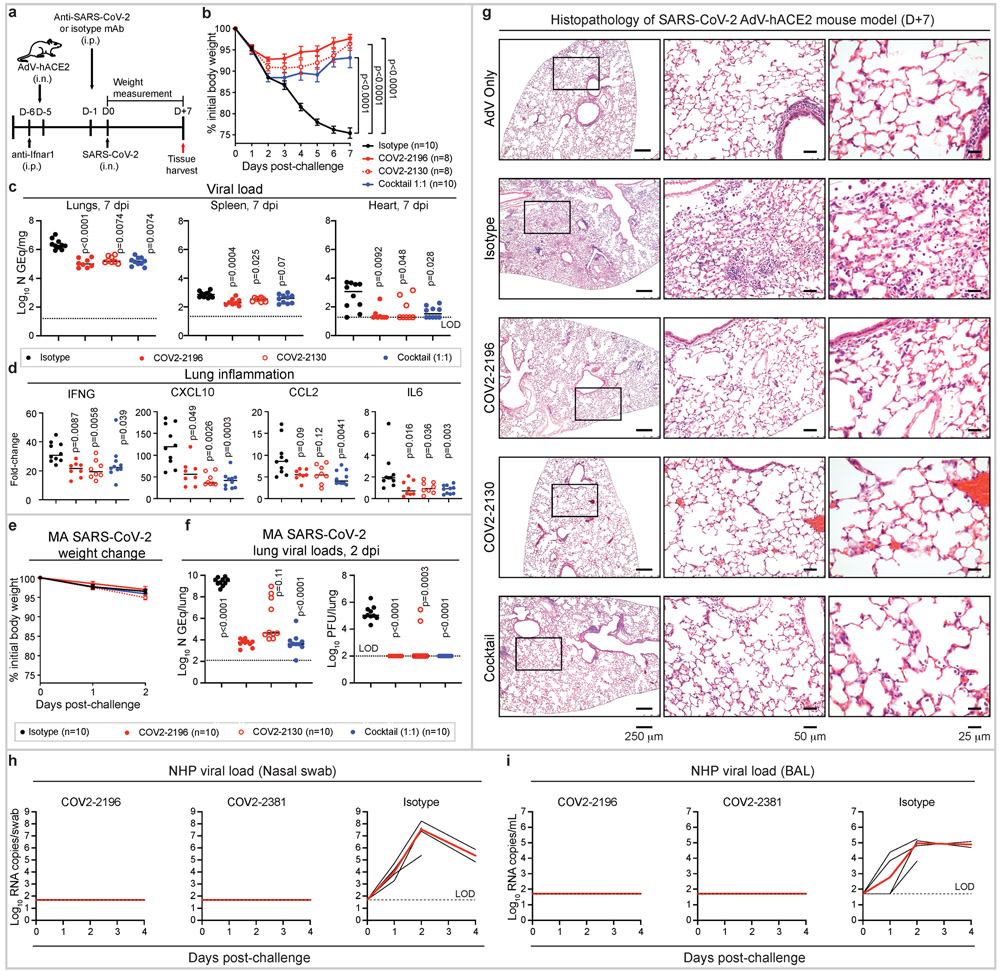
Figure 4. Prophylactic efficacy of neutralizing human mAbs against SARS-CoV-2 infection in mouse and NHP models in vivo.
a. SARS-CoV-2 challenge model. Mice were treated with anti-Ifnar1 mAb, transduced with AdV-hACE2, and 200 μg of mAbs COV2-2196, −2130, or combination (1:1 ratio) or isotype control mAb were passively transferred. One day later, SARS-CoV-2 was inoculated via the i.n. route. Tissues were harvested at 7 dpi for analysis (c, d).
b. Body weight change of mice in (a) with comparison to isotype control using a repeated measurements two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test. Mean ± SEM of each experimental group is shown. Numbers of animals (n) for each experimental group are shown.
Viral burden in the lung, spleen and heart (c) and cytokine and chemokine gene expression (d) were measured by RT-qPCR assay. Comparisons were performed using a Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA with Dunn’s post-test.
e. MA-SARS-CoV-2 challenge model. Mice were treated with indicated mAb and then infected intranasally with MA-SARS-CoV-2. Body weight change of mice is shown. Mean ± SEM of each experimental group is shown.
f. Viral burden in the lung was measured at 2 dpi by RT-qPCR (left) or plaque assay (right) from (e); comparisons were made using a Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA with Dunn’s post-test.
g. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of lung sections from mice that were treated and challenged as in (a). Images show low- (left), medium- (middle), and high-power magnification (right). Each image is representative of two separate experiments (n = 3 to 5 mice per group).
h-i. SARS-CoV-2 NHP challenge model. Animals received one 50 mg/kg dose of mAb COV2-2196 (n=4 NHPs per group) or mAb COV2-2381 (n = 4 NHPs per group) or isotype mAb (n = 4 NHPs per group) served as a contemporaneous control intravenously on day −3 and then challenged intranasally and intratracheally with SARS-CoV-2 in three days. Subgenomic viral RNA levels were assessed in nasal swabs (h) and the bronchioalveolar lavage (i) at multiple timepoints following challenge. Each black curve shows an individual animal, with red lines indicating the median values of animals within each treatment group. Data represent a single experiment. Dashed lines indicate assay limits of detection.