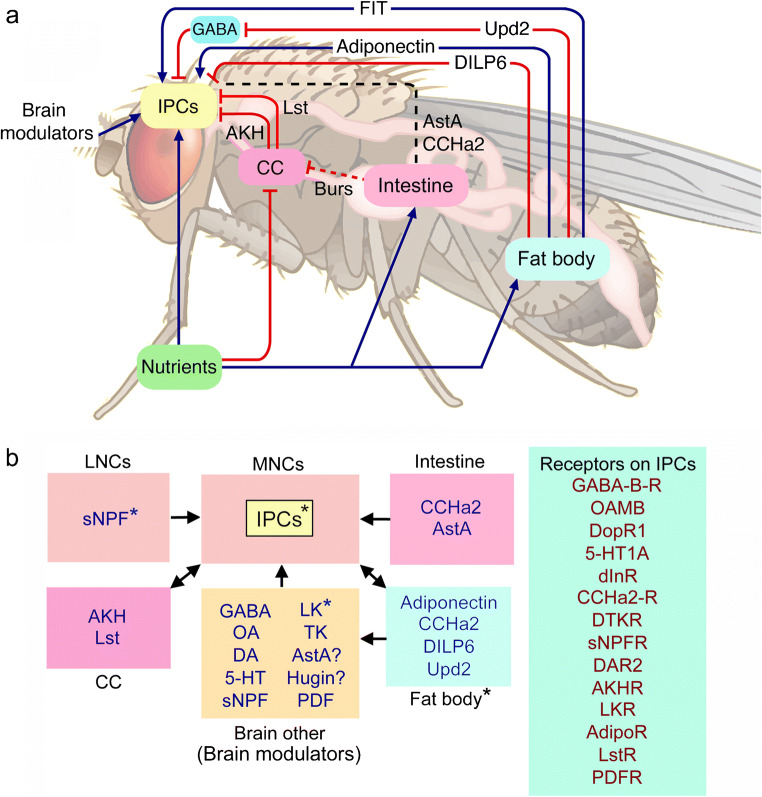
Fig. 4.
Interorgan communication: regulation of insulin-producing cells (IPCs) in Drosophila. a Scheme with factors that regulate insulin-producing cells (IPCs) in the adult brain of Drosophila. Blue arrows depict stimulatory inputs and red bars show inhibitory ones. Dashed black line indicates incompletely known mechanisms. The IPCs are also regulated by neurons in the brain (brain modulators; see panel b for details). The fat body is nutrient sensing and releases adiponectin-like polypeptide, Upd2 (unpaired-2), and DILP6 after carbohydrate intake. Adiponectin and DILP6 act directly on the IPCs. Upd2 acts (inhibitory) on GABAergic brain neurons and thereby lifts inhibition of the IPCs. Another factor FIT (female-specific independent of transformer) is a signal released from the fat body after a protein meal. The corpora cardiaca (CC), under conditions of low sugar, releases limostatin (Lst) and adipokinetic hormone (AKH) and thereby inhibits release of DILPs. The intestine has nutrient-sensing enteroendocrine cells and there is release of at least some peptide hormones into the circulation. Two gut peptides have been shown to act on IPCs, allatostatin A (AstA), and CCHamide2 (CCHa2), whereas bursicon (Burs) from the intestine acts on brain neurons, which in turn act on CC to diminish AKH production (dashed line indicates indirect action via brain). Acronyms or peptides are given in Table 1. For references to the original data, see the text. This figure is slightly modified from Nässel and Zandawala et al. (2019) with permission. b Block diagram of factors acting on IPCs and receptors expressed on these cells. The IPCs are nutrient sensing, as are peptidergic cells in the brain and fat body (asterisks). Insulin-like peptides (DILPs) released from IPCs act on CC and fat body and regulate AKH and DILP6 release, respectively. Receptor acronyms: GABA-B-R, metabotropic GABA receptor; OAMB, octopamine receptor (mushroom body); DopR1, dopamine receptor 1; 5-HT1A, serotonin receptor 1A; dInR, insulin receptor; DTKR, TK receptor; DAR2, AstA receptor 2; AdipoR, adiponectin receptor