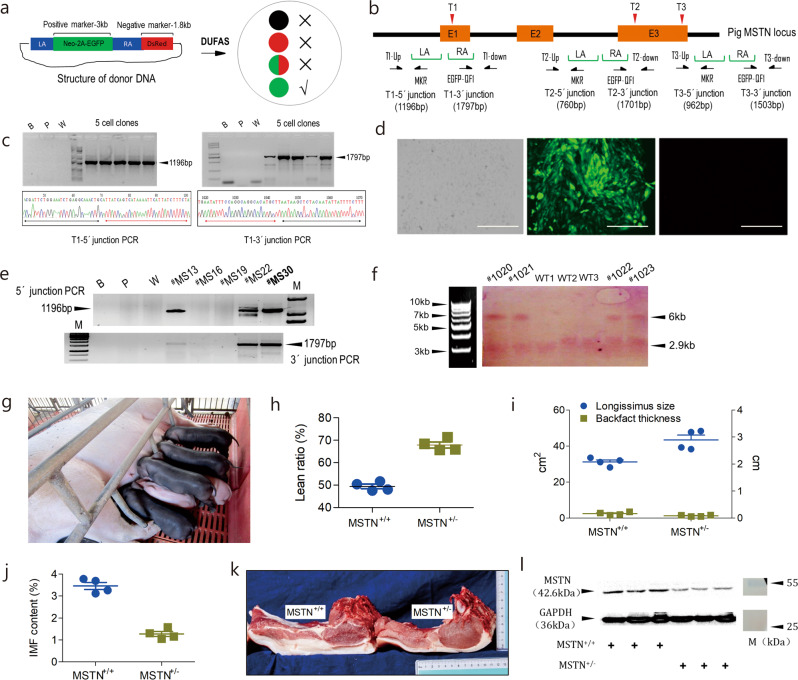
Fig. 1. Generation and phenotyping of cloned MSTN-KO Meishan pigs via DUFAS.
a Schematic of DUFAS-mediated HDR. LA, left arm. RA, right arm. “×”, non-targeted cell clones. “√”, targeted cell clones. b Outline of porcine MSTN targeting by DUFAS. LA and RA, as stated above. E1, E2, and E3 are the exons of MSTN. T1, T2, and T3 denote three CRISPR/Cas9 targeting sites. c Results of the junction PCR of targeted cell clones at the T1 site. B blank control; P negative control templated by donor DNA; W negative control templated by WT genomic DNA. Sanger sequencing results of the junction PCR are shown at the bottom. Black and red arrowheads represent the genomic sequence and homologous arm sequence, respectively. d Representative image of a targeted cell clone by DUFAS. Left, bright field. Middle, EGFP emission. Right, DsRed emission. Scale bar, 10 μm. e PCR of DNA insertion at the T1 site in the primary fetal fibroblast cells of Meishan pigs. B, P and W, defined as above. #MS16, #MS19, #MS13, #MS22, and #MS30 are five candiadte cell clones. M is 100 bp DNA ladder. f Genotyping of the newborn piglets by Southern blotting. WT wild-type genomic DNA as blotting substrate. WT1, WT2 and WT3 are three biological repeats. Black triangles denote the length of the blotted DNA fragments. The four piglets are numbered as #MS1020, #MS1021, #MS1022, and #MS1023. M is 1 kb DNA ladder (N3232L, NEB). g Image of the four cloned MSTN-KO Meishan piglets. h Lean ratio of MSTN+/+ and MSTN+/− pigs (n = 4 biologically independent animals). i Longissimus size and backfat thickness of MSTN+/+ and MSTN+/− pigs (n = 4 biologically independent animals). j IMF content of MSTN+/+ and MSTN+/− pigs (n = 4 biologically independent animals). k Transverse section of the longissimus from MSTN+/+ and MSTN+/− pigs. l MSTN expression by Western blotting in MSTN+/+ and MSTN+/− pigs. GAPDH is the internal control. M is the Page Ruler Prestained Protein Ladder 26616 (ThermoFisher Scientific).