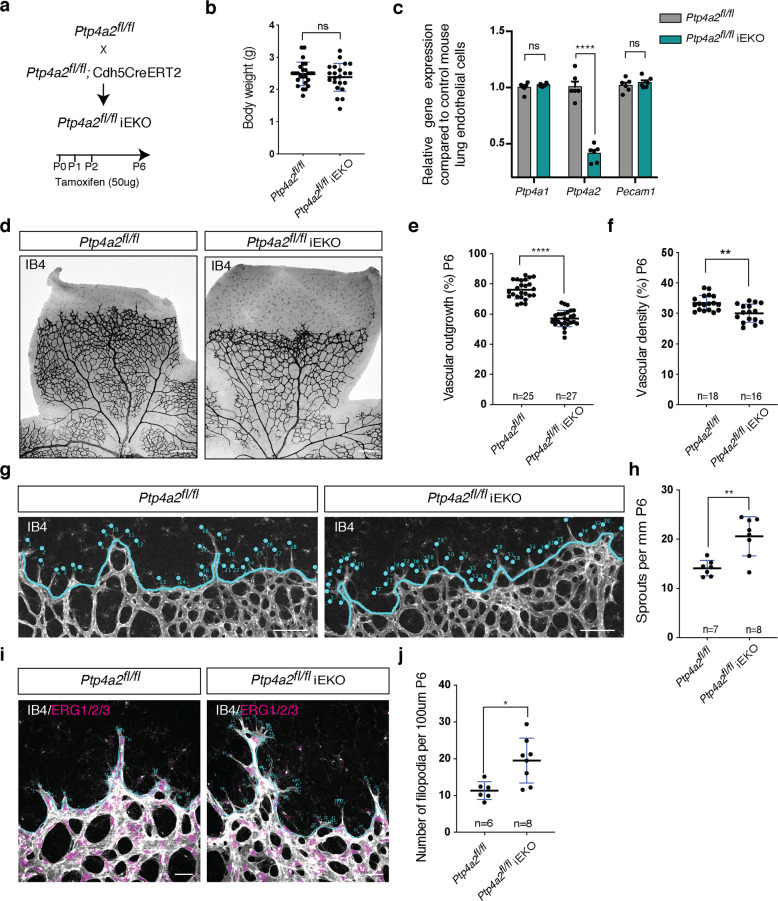
Fig. 1. Postnatal endothelial Ptp4a2 deletion impairs vascular development.
a Generation strategy for Ptp4a2fl/fliEKO mice and gene deletion through intragastric tamoxifen injection in postnatal mice. b Mice weight in P6 Ptp4a2fl/fl and Ptp4a2fl/fliEKO (Mann–Whitney U test: ns nonsignificant p value > 0.05). c qPCR analysis of mouse lung endothelial cell isolated from P6 Ptp4a2fl/fl and Ptp4a2fl/fliEKO (two-way ANOVA: ****p value < 0.0001). Each individual data point represents a mouse. d Retina whole-mount staining with isolectin B4 (IB4), and quantification of e vascular outgrowth and f density in P6 Ptp4a2fl/fl and Ptp4a2fl/fliEKO mice. Each individual data point represents a mouse (average of two retinas) (Mann–Whitney U test: **p value < 0.01, ****p value < 0.001). g Retina whole-mount staining with isolectin B4 and high magnification of vascular front. h quantification of the number of sprouts in P6 Ptp4a2fl/fl and Ptp4a2fl/fliEKO mice. Each individual data point represents a mouse i high magnification of retina whole mounts stained with IB4/ERG1/2/3 and j filopodia quantification per sprout (Mann–Whitney U test: *p value < 0.05, **p value < 0.01). Each n represents individual mouse. Scale bars: d 250 μm, g 100 μm, i 25 μm. Error bars represent mean ± s.e.m.