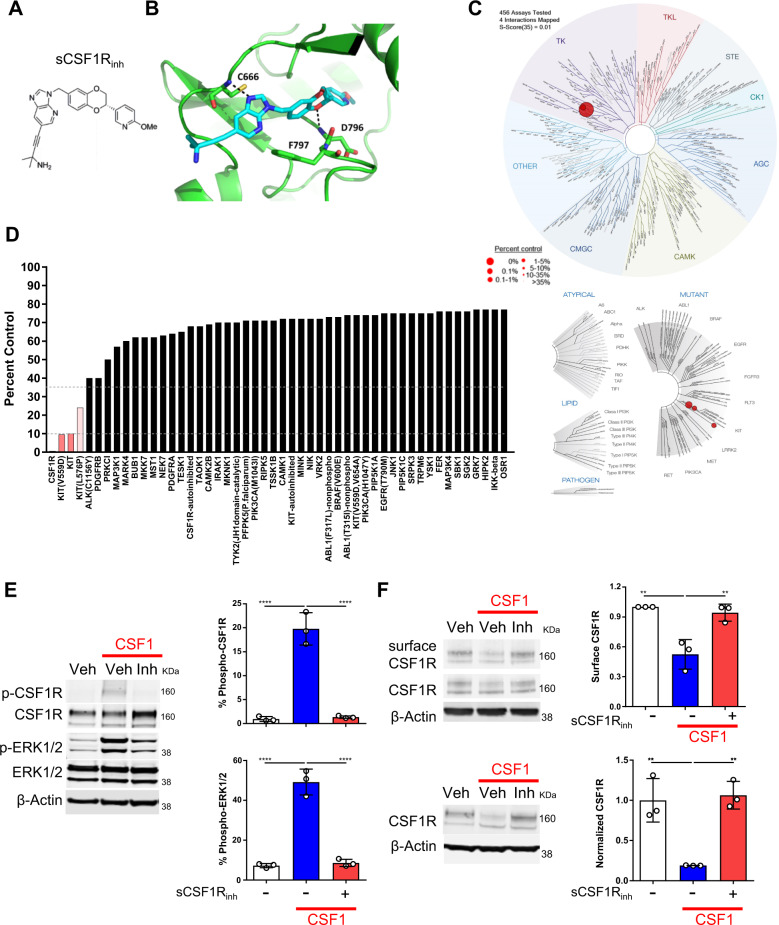
Fig. 3. Generation and validation of sCSF1Rinh, a novel small molecule CSF1R inhibitor.
a The chemical structure of the CSF1R inhibitor, ((S)-4-(3-((2-(6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-6-yl)methyl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-6-yl)-2-methylbut-3-yn-2-amine (sCSF1Rinh). b CSF1R crystal structure in combination with sCSF1Rinh shows how the inhibitor binds in a DFG-out conformation and makes key interactions with the hinge region. c TREEspot™ interaction map is an artistic representation of the human kinome phylogenetic tree. Kinases found to bind sCSF1Rinh are highlighted with red circles where larger circles indicate higher affinity binding. d KINOMEscan™ screening platform is an active site-directed competition binding assay to quantify the interaction between sCSF1Rinh and 450 human kinases. The percent control score demonstrates that sCSF1Rinh is highly selective for CSF1R. e CSF1 (100 ng/mL) stimulation of BV2 microglia induces CSF1R and ERK1/2 phosphorylation after 5 min and sCSF1Rinh (500 nM) blocks these phosphorylation events (f) After 10 min, CSF1 stimulation of BV2 microglia leads to endocytosis of the receptor and sCSF1Rinh (500 nM) maintains CSF1R surface expression. Upon endocytosis, CSF1R is trafficked to the lysosome for degradation and sCSF1Rinh (500 nM) blocks CSF1R degradation. Data points represent quantification from a single Western Blot. Graphical columns represent the mean and standard deviation of biological triplicates. Statistical significance was determined by a one-way ANOVA and p values are indicated by ****p < 0.0001.