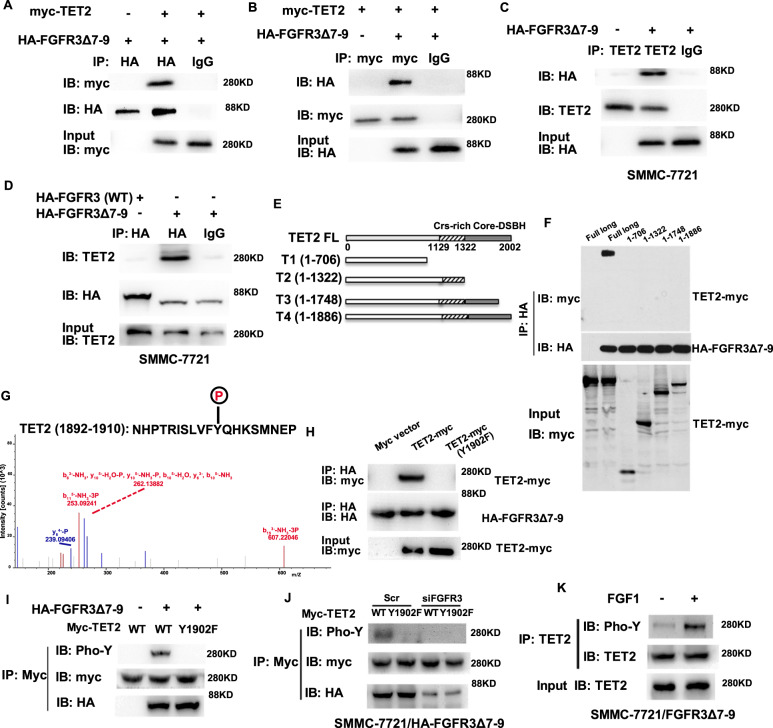
Fig. 1. FGFR3∆7–9 phosphorylates TET2 at Y1902.
A–B Immunoprecipitates (IP) from 293T cells transfected with HA-FGFR3∆7–9, myc-TET2, or both plasmids. C–D Immunoblot analysis of immunoprecipitation from SMMC-7721 cells stably expressing the HA-FGFR3∆7–9 construct. E The truncated versions of TET2, T1 (1–706 aa), T2 (1-1322), T3 (1-1748), and T4 (1-1886). F The interactions between FGFR3∆7–9 and truncated versions of TET2 were determined by immunoprecipitation. G The tyrosine phosphorylation site of TET2 was measured by Multistage mass spectrometry in SMMC-7721 cells stably expressing the HA-FGFR3∆7–9 construct; H SMMC-7721 cells were transfected with myc-WT-TET2 or myc-Y1902F-TET2, together with HA-FGFR3∆7–9. I TET2 tyrosine phosphorylation status was examined by immunoblot analysis after immunoprecipitation by anti-Myc (Myc-TET2). J TET2 phosphorylation status was detected in indicated cell lines. K TET2 phosphorylation status in SMMC-7721FGFR3∆7–9 cells in the presence and absence of FGF1.