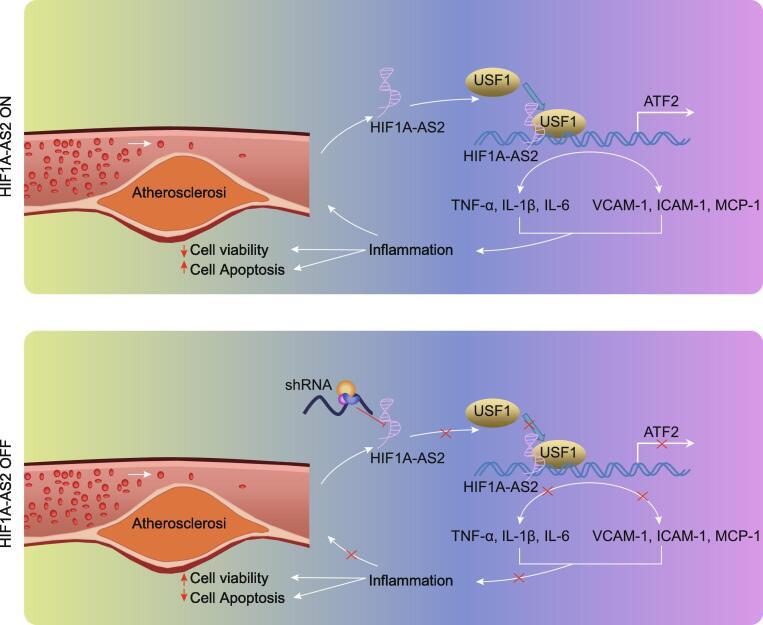
Fig. 8.
The map illustrating mechanisms associated with lncRNA HIF1A-AS2-mediated inflammation in the atherosclerosis. The upper panel shows that lncRNA HIF1A-AS2 forms a complex with USF1, which is then recruited into the ATF2 promoter to elevate ATF2 expression, thus promoting the development of atherosclerotic inflammation. The lower panel shows that downregulation of lncRNA HIF1A-AS2 reduces the expression of ATF2 by reducing the binding of USF1 to the ATF2 promoter regions, thereby inhibiting atherosclerotic inflammation, corresponding to decreased inflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 in serum and protein levels of adhesion molecules VCAM-1, ICAM-1, and MCP-1, as well as increased cell viability and reduced apoptosis in ox-LDL-induced inflammation in ECs, SMCs, and HCAECs.