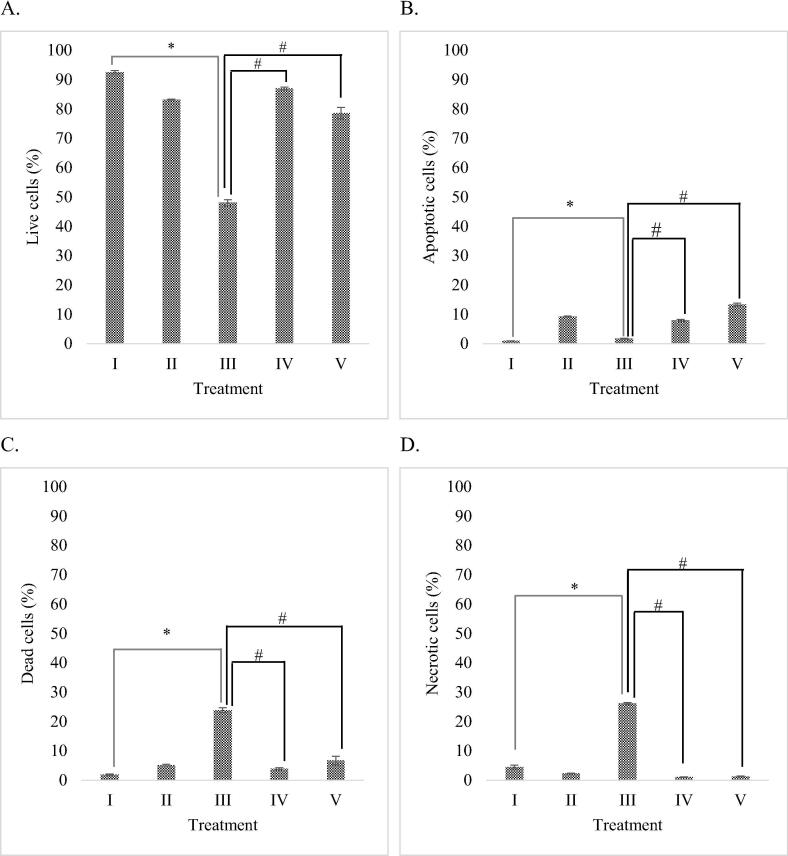
Fig. 2.
Effect of RBLE towards apoptosis inducing activity of H2O2-induced HepG2 cells. (A) Live cells (%); (B) Apoptotic cells (%); (C) Dead cells (%); (D) Necrotic cells (%). *Data is presented as mean ± standard deviation. (I): Control (untreated HepG2 cells); (II): Vehicle control (HepG2 cells + DMSO 1%); (III) LI model (Liver Injury model; H2O2-induced HepG2 cells); (IV) RBLE25 (H2O2-induced HepG2 cells + RBLE 25 μg/mL); (V) RBLE100 (H2O2-induced HepG2 cells + RBLE 100 μg/mL). Single star sign (*) marks statistical difference between control and Liver Injury (LI) model group at 0.05 significance level, single hashtag (#) marks statistical difference for treatment groups compared to Liver Injury (LI) model group at 0.05 significance level.