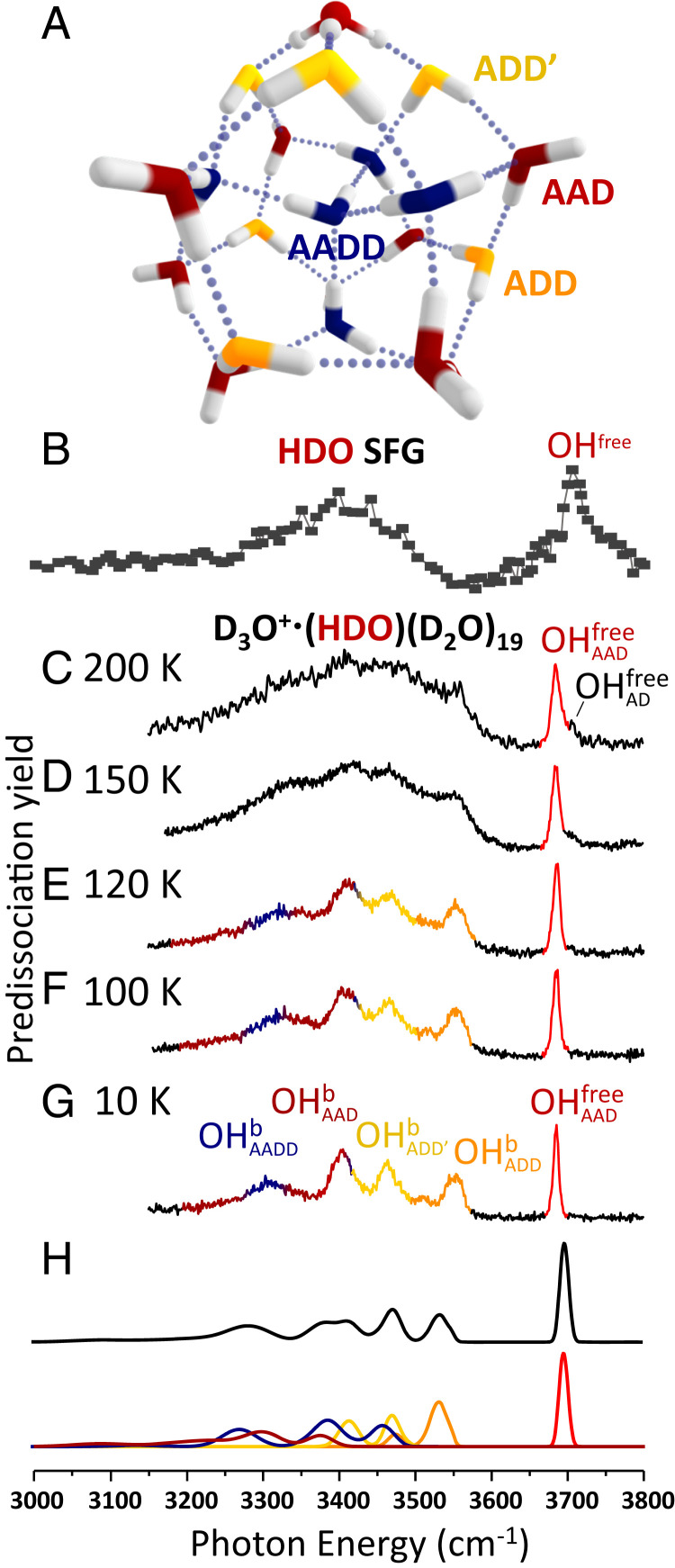
Fig. 1.
Comparison of the isotope-diluted SFG spectrum of the air–water interface with vibrational predissociation spectra of D3O+∙(HDO)(D2O)19 at temperatures in the range 10 to 200 K. (A) Representative low-energy structure of the H3O+∙(H2O)20 cluster. The stick spectra of the clusters with the OH group in each of the possible sites of the cluster are included in SI Appendix, Fig. S2. (B) SFG spectrum of HDO at the air–water interface. Reprinted with permission from ref. 5. Copyright 2009 American Chemical Society. (C–G) Vibrational spectra of D3O+∙(HDO)(D2O)19 from 200 to 10 K. OHb and OHfree represent hydrogen-bonded OH and free OH. The A/D notation labels the number of hydrogen bond acceptors and donors on one water molecule. H displays the calculated spectrum based on 400 isotopomers of the 10 lowest energy structural isomers of the D3O+∙(HDO)(D2O)19 cluster. The contribution from each type of water molecule (or site) to specific regions of the spectrum is colored to match the scheme in A.