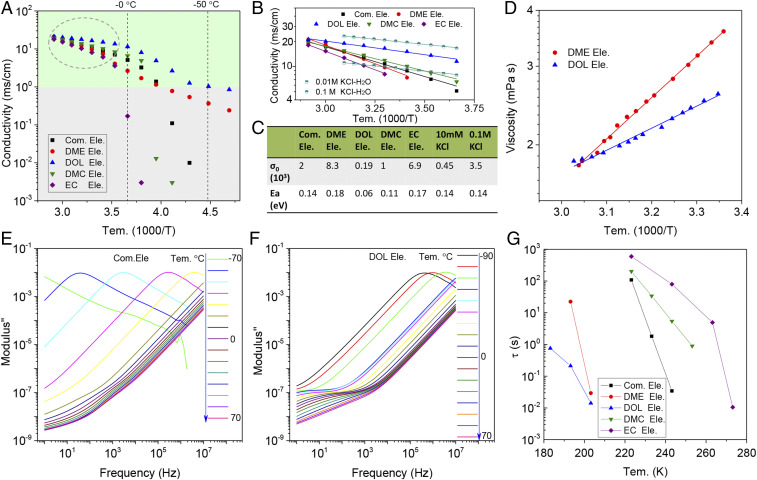
Fig. 1.
Ion-transport characteristics in electrolytes comprising different solvents. (A) DC conductivity versus temperature. The commercial electrolyte (Com. Ele.) is composed of 1 M LiPF6 dissolved in a symmetric EC/DMC (1:1 by volume) solvent blend. The electrolytes designated DME, DOL, DMC, and EC are each composed of a 2 M LiFSI salt dissolved in the respective solvents. (B) Arrhenius fitting of the measured ionic conductivity versus temperature at relatively high temperatures. Results for aqueous KCl electrolytes are also listed to facilitate comparisons. (C) Arrhenius preexponential factor (σ0) and Ea diffusion calculated from the fits in B for all electrolytes used in the study. (D) Arrhenius fits of the shear viscosity versus temperature data for DOL and DME-based electrolytes. Dielectric loss modulus spectra as a function of temperature for electrolytes composed of (E) 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC and (F) 2 M LiFSI in DOL. (G) Variation in characteristic relaxation times (τ) as a function of temperature. τ was obtained by fitting the frequency-dependent dielectric modul measured at each temperature using the H-N function.