FIG 4.
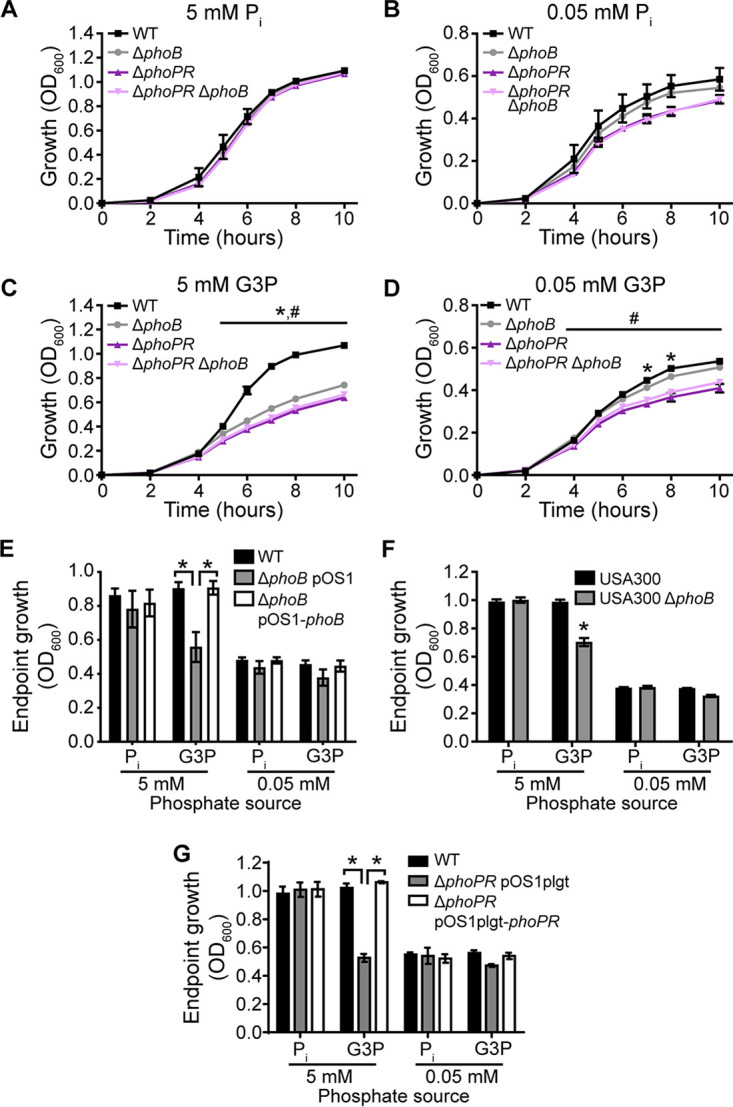
PhoB is important for the use of G3P as a phosphate source. (A to D) Growth of wild-type S. aureus (Newman) and the indicated mutants in PFM9 with 0.5% glucose supplemented with the phosphate source Pi (A and B) or G3P (C and D) in excess (A and C) or limiting (B and D) amounts. *, P < 0.05 for the ΔphoB mutant compared to the wild type; #, P < 0.05 for the ΔphoPR mutant compared to the ΔphoB mutant (by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test) (n = 4). (E) Endpoint growth after 10 h of wild-type S. aureus with an empty vector (pOS1), the ΔphoB mutant with an empty vector, or the ΔphoB mutant with a vector containing phoB in PFM9 with 0.5% glucose and the indicated concentrations of Pi or G3P as the phosphate source. *, P < 0.05 for the indicated comparison by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test (n = 3). (F) Endpoint growth after 10 h of wild-type S. aureus USA300 (JE2) or the ΔphoB mutant in PFM9 with 0.5% glucose supplemented with the indicated concentrations of Pi or G3P as the phosphate source. *, P < 0.05 for the phoB::erm strain compared to the wild type by two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple-comparison test (n = 3). (G) Endpoint growth after 10 h of wild-type S. aureus with an empty vector (pOS1), the ΔphoPR mutant with an empty vector, or the ΔphoPR mutant with a vector containing phoPR in PFM9 with 0.5% glucose and the indicated concentrations of Pi or G3P as the phosphate source. *, P < 0.05 for the indicated comparison by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test (n = 3). For panels A to G, strains were precultured overnight in TSB. Error bars indicate SEM.
