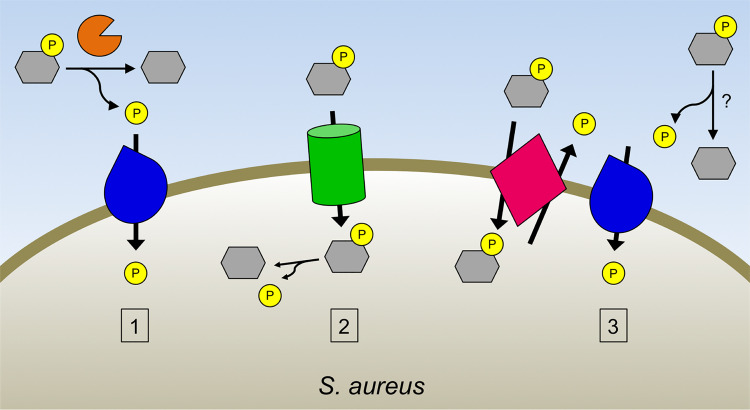
FIG 7.
Model of phosphate acquisition from alternative phosphate sources by S. aureus. S. aureus can acquire phosphate from a variety of phosphosubstrates during phosphate starvation through three pathways: the alkaline phosphatase PhoB (orange) cleaves Pi (yellow) from phosphorylated compounds (gray) extracellularly, with the liberated Pi subsequently imported by Pi importers (blue) (pathway 1); phosphorylated molecules can be imported intact through phosphosubstrate importers (green), with Pi subsequently released intracellularly (pathway 2); and extracellular Pi is generated independently of PhoB, such as by phosphosubstrate/Pi antiporters (pink) or by other phosphatases, which is then imported through Pi importers (pathway 3).