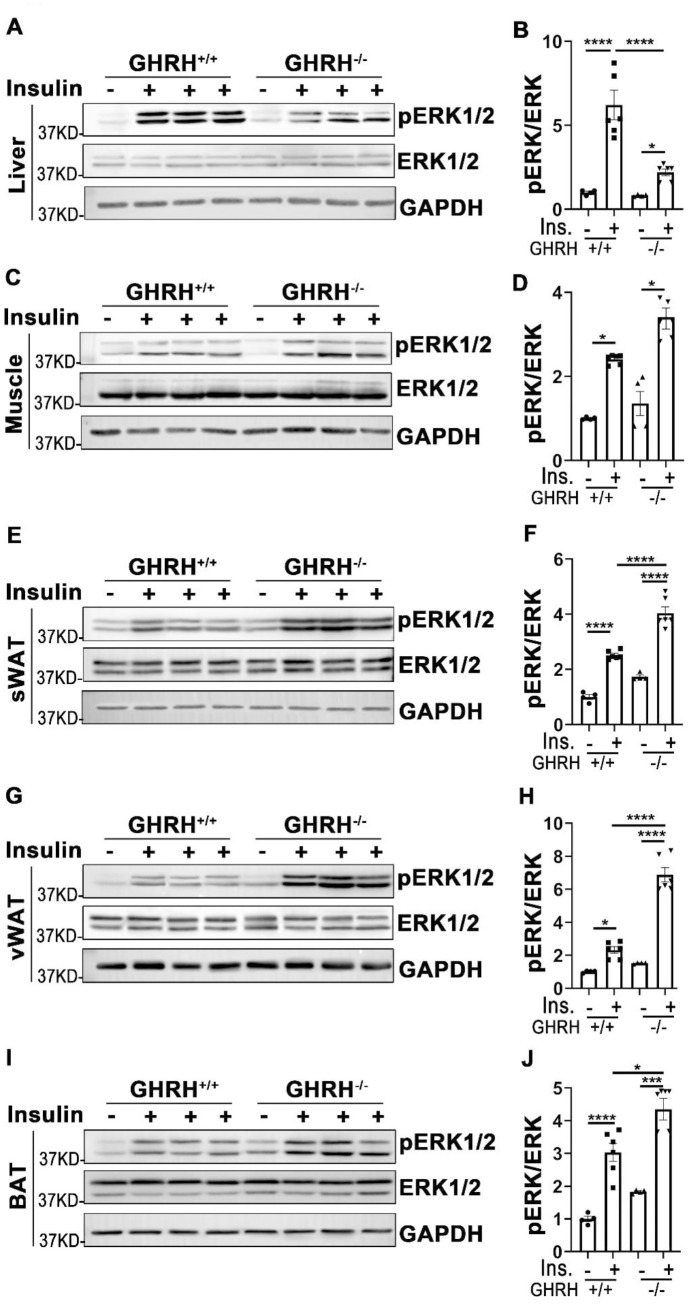
Figure 5.
Analysis of insulin-induced activation of ERK1/2 in metabolically active tissues of GHRH-/- mice. (A, B) Activation of ERK1/2 in liver. (C, D) Activation of ERK1/2 in skeletal muscle. (E, F) Activation of ERK1/2 in subcutaneous white adipose tissue. (G, H) Activation of ERK1/2 in visceral white adipose tissue. (I, J) Activation of ERK1/2 in interscapular brown adipose tissue. The 4 hours fasted mice were injected i.p. with porcine insulin (1 IU/kg of body weight). After 20 min, tissues were collected to perform western blots. All data (means ± sem) were expressed as fold change compared to vehicle treated WT controls (defined as 1.0) (n=4 for WT group; n=6 for GHRH-/- mice). Statistical analysis was performed by unpaired Student’s t-test, * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001 and **** P < 0.0001.