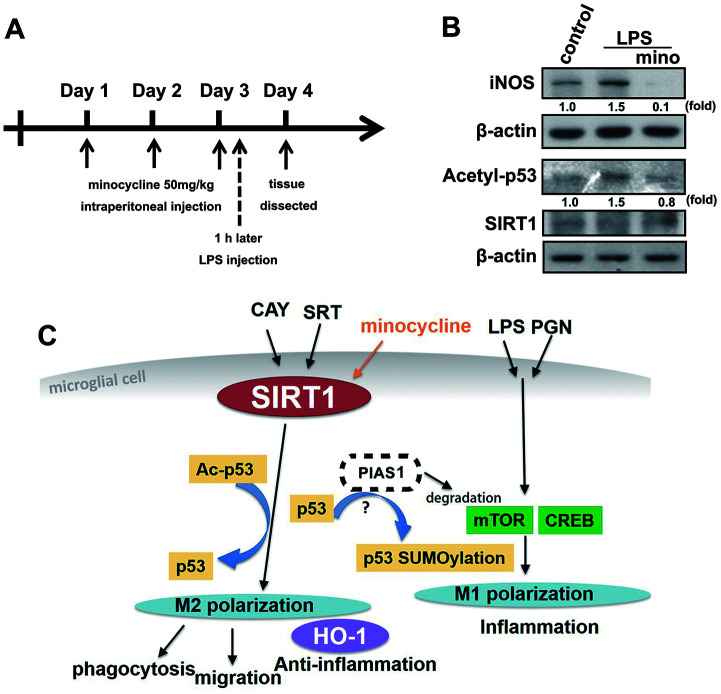
Figure 9.
The protective effect of minocycline prevents LPS-induced acetylation of p53 in a mouse model. (A) Schematic representation of the protocol for minocycline and LPS administration. Mice were treated with either minocycline (50 mg·kg−1) or vehicle, once daily for three consecutive days, before a single intraperitoneal injection of LPS (20 mg·kg−1). LPS was administered to mice on the third day 1 h after minocycline administration. (B) The mice were sacrificed, and their brain cortex were dissected 1 day after LPS injection and analyzed by western blot to assess the presence of the indicated proteins. (C) The schema of the regulatory mechanism of minocycline on SIRT1 and p53 in microglial polarizations.