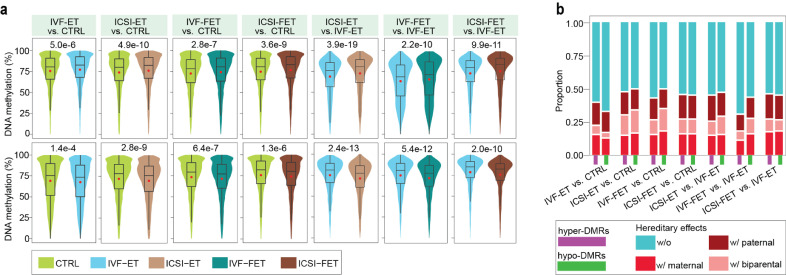
Fig. 2.
Removal of the parental effects in neonatal DMRs. (a) Violin-box plots displayed the distribution of DNA methylation level in paternal samples at hyper- (upper) and hypo-DMRs (lower) of the seven comparisons, IVF-ET versus CTRL, ICSI-ET versus CTRL, IVF-FET versus CTRL, ICSI-FET versus CTRL, ICSI-ET versus IVF-ET, IVF-FET versus IVF-ET, and ICSI-FET versus IVF-ET neonatal samples. The p-value between two groups was determined by Wilcoxon rank-sum test. (b) Bar graph showed the proportion of DMRs with/without hereditary effects in the hyper- or hypo-DMRs of each comparison. Any one of the 14 groups of DMRs were classified into four subgroups, without hereditary effects (w/o), only with paternal hereditary effects (w/paternal, only overlapped with the DMRs of comparison for the corresponding fathers), only with maternal hereditary effects (w/ maternal, only overlapped with the DMRs of comparison for the corresponding mothers), and with biparental hereditary effects (w/ biparental, overlapped with the DMRs of comparisons for the corresponding fathers and mothers).