Fig. 1.
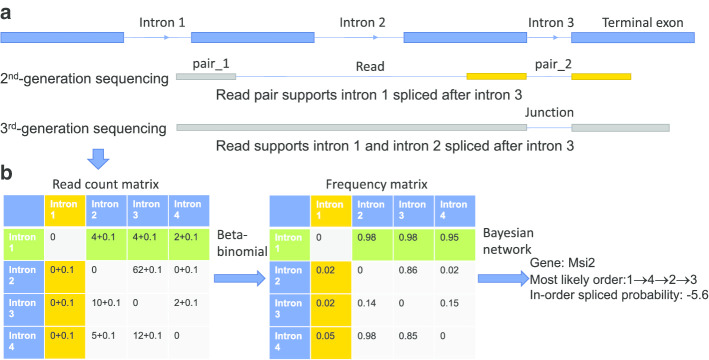
Methodology overview. a Sequencing methods that can detect intron splicing order pairs used by previous studies. From top to bottom: gene structure; short-read pair; long-read sequencing read. b The number in the adjacent matrix is the read count that supports each intron splicing order pair; the row was spliced before the column; the value within [i, j] records the read count of intron i spliced before intron j. The + 0.1 in the matrix is the pseudo read count. The right-most part of b represents the calculated most likely intron splicing order for this transcript, and the log relative likelihood indicates the probability that this transcript is spliced in an order that is consistent with transcription, i.e., 1 → 2 → 3 → 4