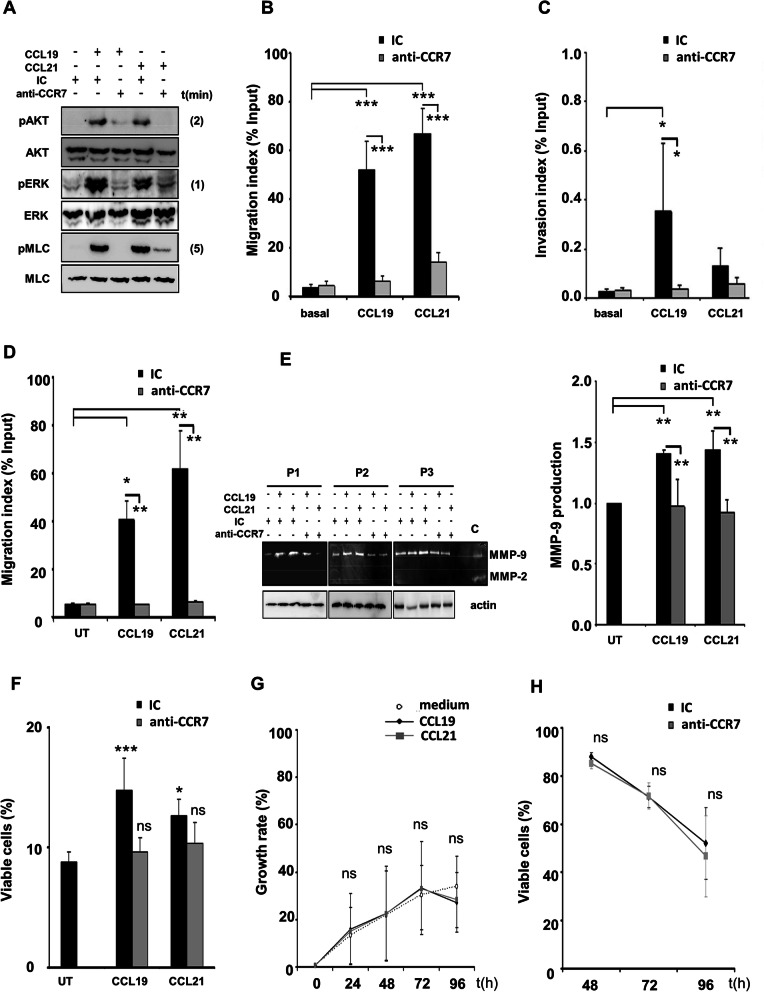
Fig. 2.
Blocking CCR7 neutralizes target-mediated cell functions on T-PLL. a Anti-CCR7 mAb blocks CCR7 activation and signal transduction in T-PLL cells. Serum-starved T-PLL cells were pre-treated with 10 μg/mL of anti-CCR7 or the respective IC for 30 min and then treated with CCL19 or CCL21 for different time points. Cell extracts were analyzed by Western blot. The figure shows representative blots from 6 independent experiments. b Anti-CCR7 mAb neutralizes CCR7-mediated T-PLL cells migration in response to CCL19 and CCL21. Chemotaxis of T-PLL cells induced by CCL19 and CCL21 was assayed in uncoated transwell chambers for 4 h. When indicated, cells were pre-treated with 10 μg/mL of anti-CCR7 mAb or the respective IC (n = 6). c Blocking CCR7 abrogates T-PLL cells invasion driven by CCL19 and CCL21. T-PLL cells with or without previous incubation with anti-CCR7 mAb or the matching IC were embedded in Matrigel™ before exposure to chemokines for 24 h. Values represent the percentage of migrated cells referred to the total cells added (n = 4). d Anti-CCR7 mAb inhibits target-mediated T-PLL cells migration across endothelium. T-PLL cells were incubated on the upper chamber of transwell filters coated with TNFα-activated HUVEC, in the presence or absence of the indicated mAbs. Then chemokines were added and after 4 h, the cells were counted by flow cytometry. Values represent the percentage of migrated cells referred to the total cells added (n = 4). e Anti-CCR7 mAb reduces target-mediated MMP-9 secretion. CCR7 engagement up-regulates MMP-9 in T-PLL cells. Leukemic cells from 3 different patients (P1, P2 and P3) were pre-treated with anti-CCR7 mAb or an IC (10 μg/mL) and then incubated with/without CCL19 or CCL21 (1 μg/mL) for 24 h. The concentrated conditioned media were analyzed by gelatin zymography to detect MMP-2 and MMP-9 secretion. MMP-9 was identified as the 92-kDa proactive form. Cell pellets of each point were lysed and cell extracts were used to detect actin by Western blotting as loading control (C, fetal bovine serum (FBS) used as positive control showing the degradation bands of active MMP-9 and MMP2). The average quantification of MMP-9 secretion (arbitrary units) for the 3 samples studied is given; basal levels of MMP-9 on bovine serum albumin (BSA) and without chemokines were normalized to 1. f Anti-CCR7 mAb affects target-induced pro-survival signaling pathways. CCR7 ligands increase T-PLL cells survival, a process blocked by anti-CCR7 mAb. Cells from 4 patients were incubated in 1% FBS medium alone or with CCR7 ligands (1 μg/mL) for 72 h. Where indicated, cells were also incubated in the presence of 10 μg/mL of anti-CCR7 mAb or an IC. The percentage of viable 7-AAD− Annexin-V− cells at 72 h is shown. g CCR7 ligands do not induce proliferation of T-PLL cells. T-PLL cells (n = 5) were harvested and stained with CellTrace™ Violet reagent. Then, 5 × 105 cells were cultured with 1% FBS complete medium alone or supplemented with CCL19 or CCL21. Every 24 h the successive generations of live cells were analyzed. h Anti-CCR7 mAb does not induce direct apoptosis on T-PLL cells. Leukemic cells were incubated with anti-CCR7 (10 μg/ml) or the corresponding IC in complete medium with 10% FBS (n = 5). Every 24 h the effect of the antibody was studied by Annexin-V/7-AAD double staining. In B, C, D, E, F, G, H, bars (or symbols) represent mean ± SEM. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ns, not significant