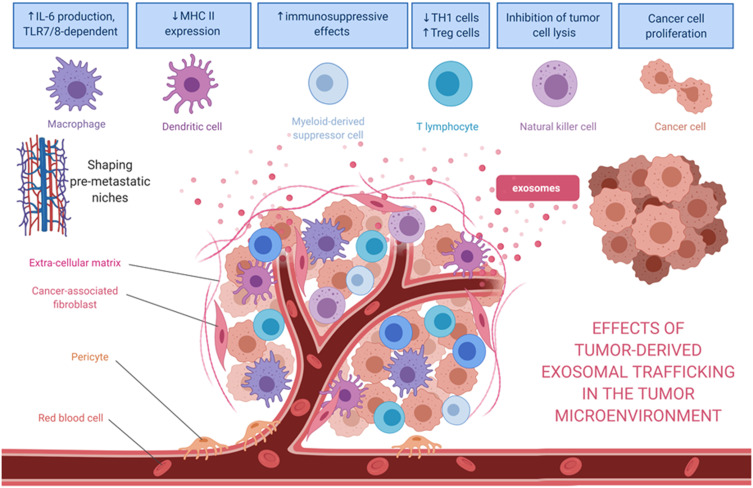
Figure 2.
Effects of tumor-derived exosomes and their horizontal paracrine trafficking to impact on the tumor microenvironment. For example, breast cancer-derived exosomes modify the TME through the suppression of T-cell proliferation and NK cell cytotoxicity. Also, the exosomal content (eg, miR-1246 or miR-155) might contribute to the chemoresistance or hormone-resistance in tumor cells. Exosomes secreted by liposarcoma cells containing miR-25-3p and miR-92a-3p have been found to stimulate IL-6 secretion in tumor-associated macrophages, leading to liposarcoma progression. miR-34a in the released exosomes enhances the neural differentiation of Ewing sarcoma. Myeloma-derived exosomes could modify the microenvironment, affecting various recipient cells such as bone marrow endothelial cells or myeloid‐derived suppressor cells. In the case of myeloma, these exosomal cargoes include miR-135b, miR18a, and let7b. After being internalized by recipient cells, miRs could bind to their target genes and trigger numerous pathways to facilitate tumor progression.