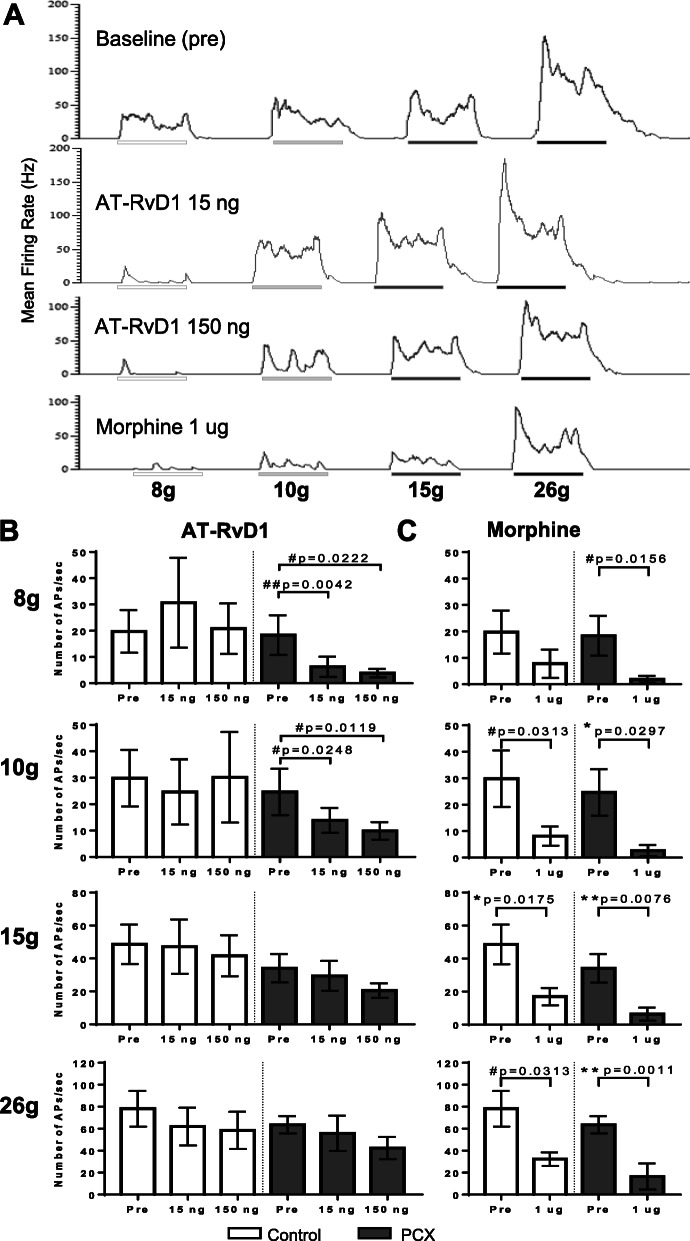
Fig. 6.
Effects of spinal AT-RvD1 versus morphine on mechanically evoked WDR neuronal responses of PCX and control rats. a Representative electrophysiological traces of mechanical (8, 10, 15 and 26 g) evoked responses of a WDR neurone of a PCX-treated rat at baseline and following the spinal application of AT-RvD1 15 ng, 150 ng and morphine 1 μg. b In PCX rats, AT-RvD1 (15 and 150 ng) dose-relatedly inhibited 8 g and 10 g, but not 15 g and 26 g, evoked responses of WDR neurones, compared to pre-drug responses (pre). AT-RvD1 had no significant effect on mechanically evoked responses of WDR neurones in control rats. Analysis with repeated measure ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test for AT-RvD1 15 and 150 ng versus pre-drug responses: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (n = 6-9/group). c Morphine suppressed low and high weight mechanical evoked responses of WDR neurones in both control and PCX rats. Analysis with either a paired t test (*) or Wilcoxon test (#) for morphine versus pre-drug responses: * or #p < 0.05,** or ##p < 0.01, (n = 6-7 neurones in each group). APs, action potentials. Most data expressed as median ± interquatile range except 15 g responses in control group; 10 g, 15 g, and 26 g responses in PCX morphine groups which data were normally distributed