Figure 3. ENH1 inhibits parasite growth through CDPK1-dependent and -independent pathways.
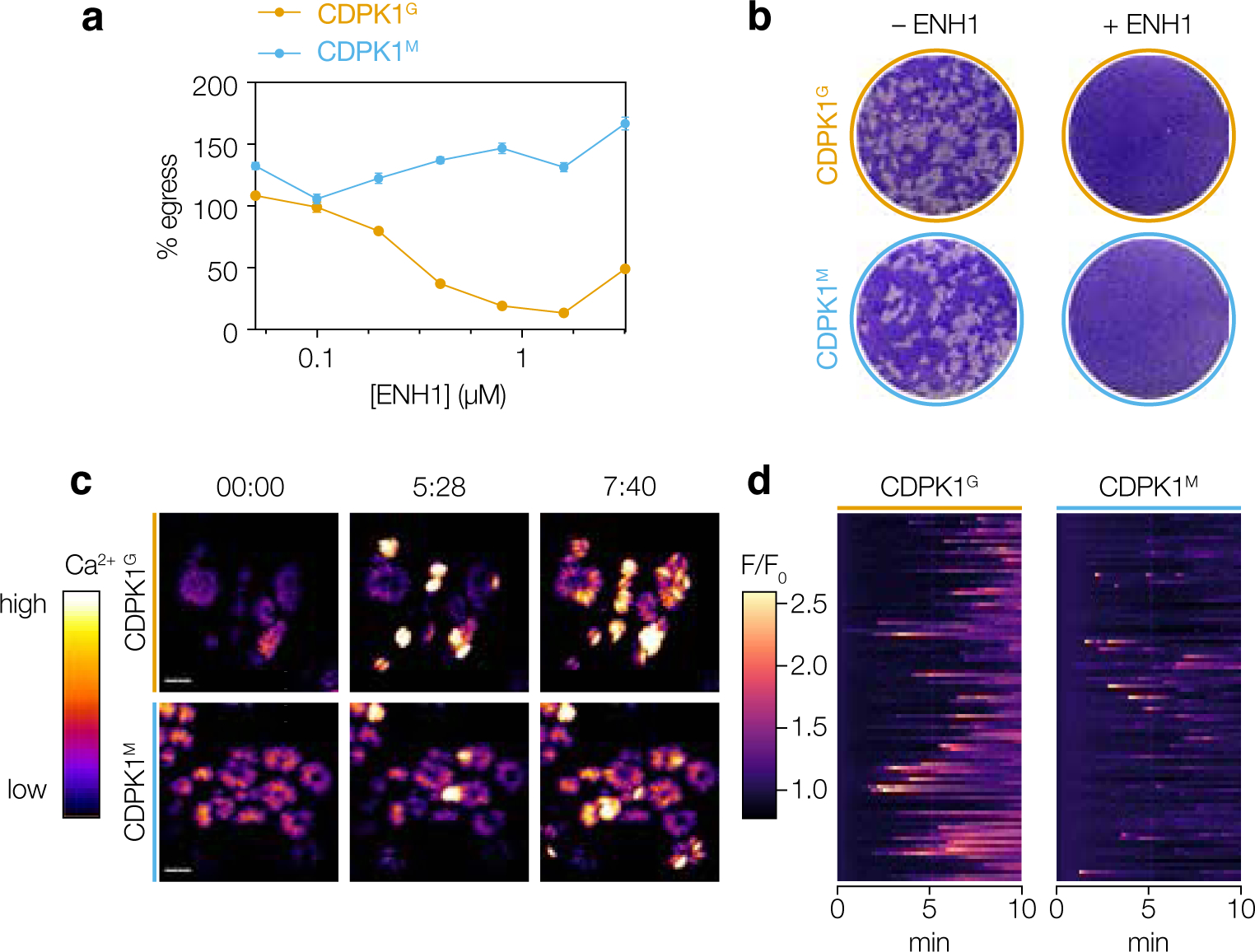
(a) Egress assays of wild-type CDPK1G and CDPK1M parasites treated with ENH1 followed by the egress agonist zaprinast. (b) Plaque assays of CDPK1G and CDPK1M parasites treated with ENH1. (c) Selected frames of time-lapse microscopy of CDPK1G and CDPK1M parasites expressing the genetically encoded calcium indicator GCaMP6f with ENH1. Scale bar is 10 μm. Time is indicated as minutes:seconds. (d) Kymographs showing the median fluorescence intensities relative to the initial intensity of 99 parasite vacuoles (rows) 10 minutes following treatment with ENH1.
