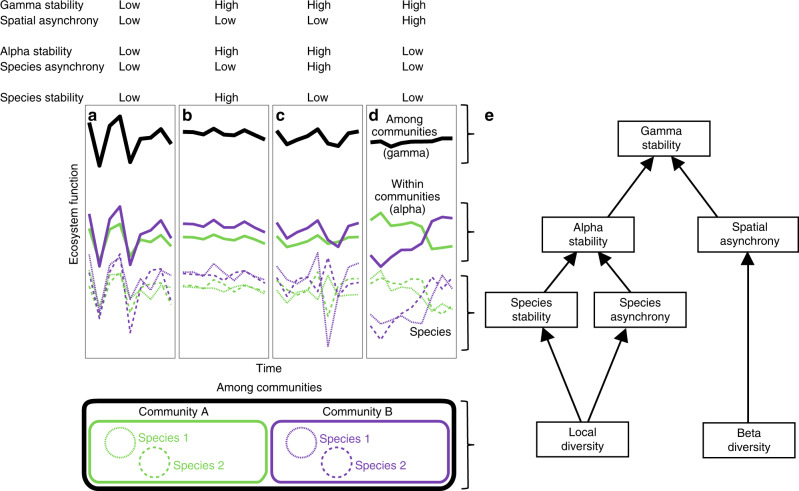
Fig. 1. Conceptual figure illustrating the nonexclusive processes by which species stability, species asynchrony, and spatial asynchrony may contribute to stabilize functioning (such as productivity) within (alpha stability) and among communities (gamma stability).
a Low stability and asynchrony of species within communities result in low alpha stability that in turn results in low gamma stability under low degree of asynchronous dynamics among communities (spatial asynchrony). Relatively high alpha and gamma stability may result from b high species stability and c high species asynchrony. d Relatively high gamma stability may additionally result from high spatial asynchrony. e Path analysis used to assess the relationship of local and beta diversity with the mechanisms promoting stability at multiple spatial scales under unmanipulated control or fertilized condition. Note that species names belong to a given community, they could or could not be the same species among communities. Adapted from Wilcox et al.21.