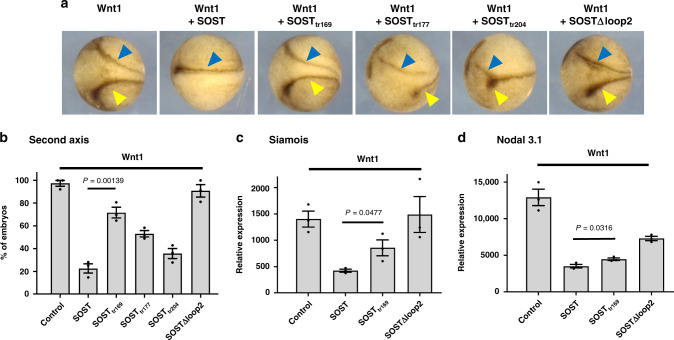
Fig. 5. Assessing the inhibitory effect of SOST on Wnt signaling in Xenopus embryos.
a The transverse dark-brown line (blue arrow) indicates the normal position of the axis. The yellow arrow indicates the position of the second ectopic axis. Wnt1 induced formation of the second ectopic axis, and successfully inhibiting Wnt resulted in the formation of a single axis. Embryos at the four-cell stage were co-injected in a ventro-vegetal blastomere with 30 pg Wnt1 mRNA (n = 104), 25 pg WT SOST mRNA (n = 106), 25 pg SOSTtr169 mRNA (n = 98), 25 pg SOSTtr177 mRNA (n = 119), 25 pg SOSTtr204 mRNA (n = 104), and 25 pg SOST∆loop2 mRNA (n = 96) (n number of embryos). b The percentage of embryos with a second axis. The error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM) from three independent experiments (n = 3) and p value by two-tailed t-test is indicated. The number of injected embryos is described in a. c, d Real-time qPCR analyses of the expression of genes directly targeted by Wnt1, namely siamois (c) and nodal 3.1 (d) from animal cap explants isolated at stage 8 and grown to stage 11. The error bars represent SEMs from three independent experiments (n = 3) and p values by two-tailed t-test are indicated.