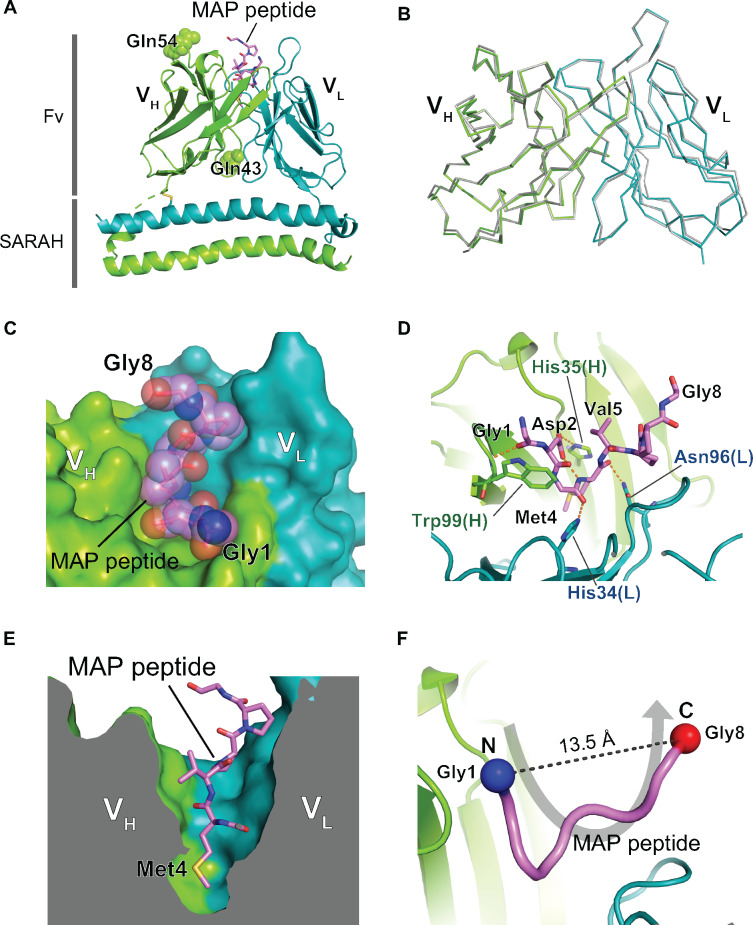
Fig. 1.
Crystal structure of the PMab-1(QQ) Fv-clasp in complex with the MAP tag peptide. (A) Overall structure of the PMab-1(QQ) Fv-clasp-MAP tag peptide complex. The VH-SARAH and the VL-SARAH are shown as cartoon presentation. The bound MAP tag peptide is shown as a stick model. The two substituted Gln residues, Gln43 and Gln54, in the VH domain are shown as sphere models. (B) Comparison of the Fv structures between the two PMab-1(QQ) Fv-clasp molecules in the asymmetric unit. The Fv region of the Mol-2 (grey) is superposed on that of the Mol-1 (coloured), and they are shown in Cα tracing. (C and D) The expanded views of the antigen binding pocket of PMab-1. PMab-1 is shown as a surface model, and the MAP tag peptide is shown as a stick model with a transparent sphere model (C). PMab-1 residues involved in the MAP tag peptide recognition are shown as stick models, and hydrogen bonds are denoted by dashed lines (D). (E) Sliced-surface view at the antigen binding pocket. Note that the side chain of Met4 of the MAP tag peptide is deeply inserted into a cavity formed between the VH and the VL. (F) U-shaped conformation of the MAP tag peptide bound by PMab-1. The MAP tag peptide is presented as a worm model. The Cα atoms of Gly1 and Gly8 are shown as sphere models.