Figure 5.
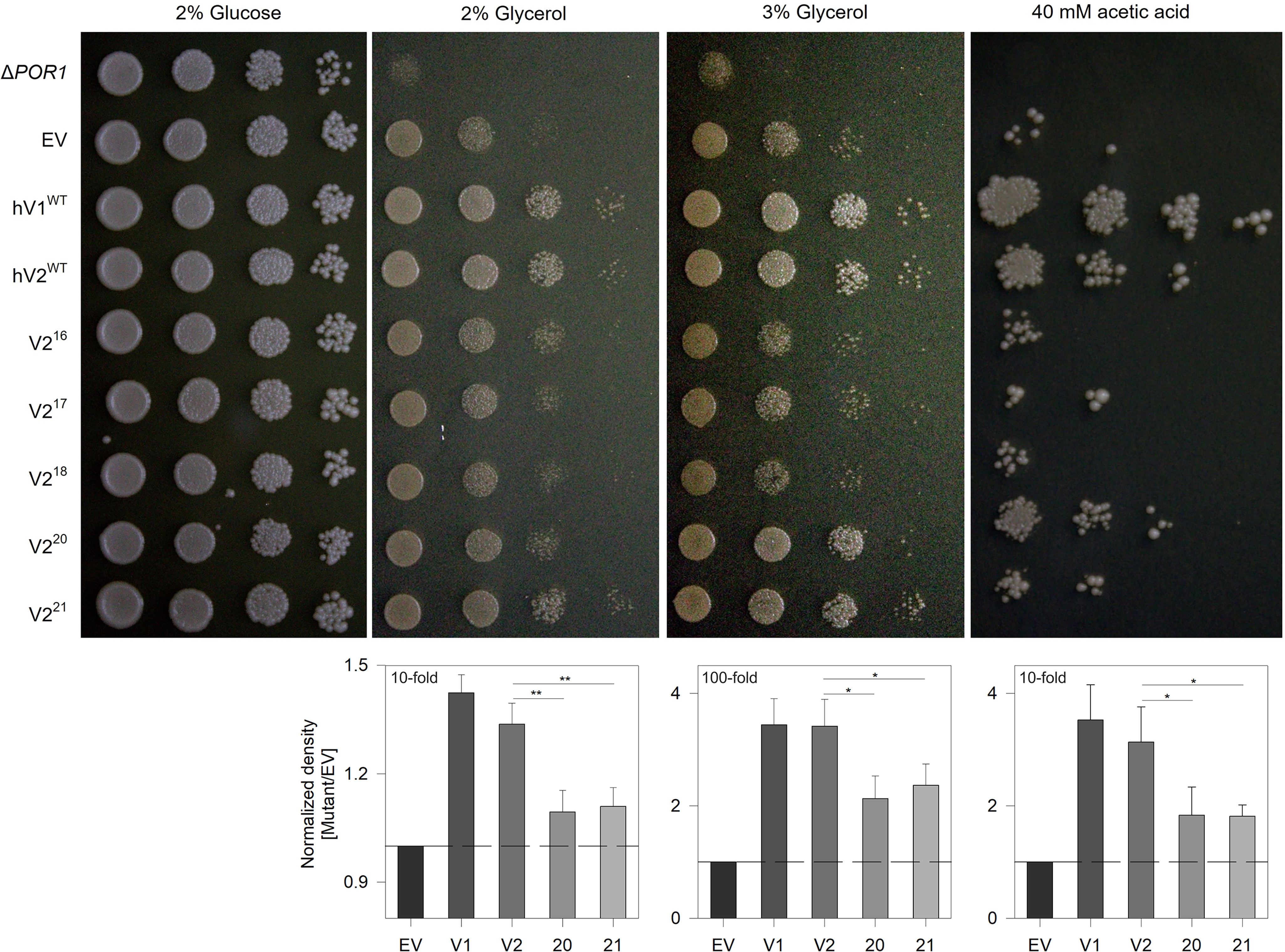
Complementation with hV2WT supports yeast survival under restrictive growth conditions. Serial spot dilution assay to measure survival efficiency of POR1-deficient yeast. ΔPOR1 yeast strain BY4742 (por1Δ) transformed with pYX212 shuttle vector (EV) carrying WT human VDAC1 (hV1WT), human VDAC2 (hV2WT), and the engineered barrels (V216–V221) were spotted (left to right, fold dilution = 0, 10, 100, and 1000) in medium containing glucose or glycerol (nutrient restriction) as the sole carbon source. The survivability of yeast expressing the VDAC variants was assessed on two glycerol concentrations, namely, 2 and 3%. The cells were also grown in glucose-containing medium additionally containing acetic acid to induce oxidative stress. Quantification obtained from spot density (2% glycerol and acetic acid, 10-fold; 3% glycerol, 100-fold) from >12 independent experiments is presented as histograms (lower panels). EV has a likely growth advantage over por1Δ, because of the additional expression of the URA3 gene (selection marker for pYX212). Therefore normalization was done in each case against the growth of EV. Statistical analysis was carried out using a one-tailed t test. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01. Note how yeast expressing strand deletion constructs show poor survival, whereas the growth of cells expressing V220 or V221 is less compared with hV1WT and hV2WT.
