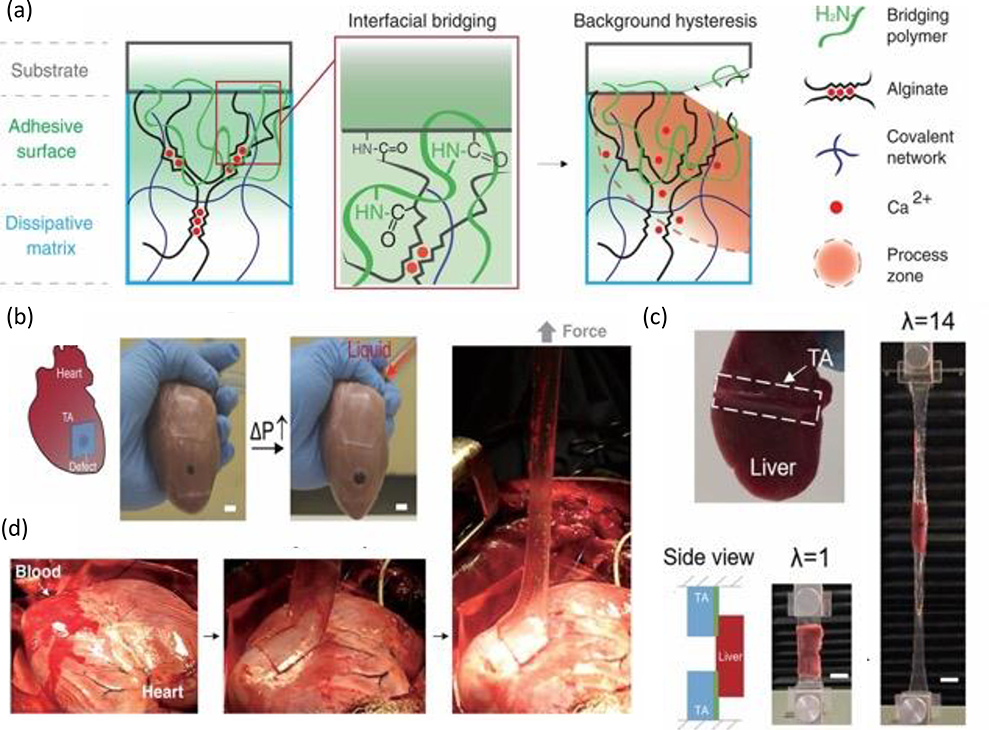
Figure 10. Tough adhesive for adhesion onto wet and dynamic surfaces.
(a) Schematic of adhesive system consisting of an adhesive surface featuring a bridging polymer with primary amines (green lines), and a dissipative matrix constructed with hydrogel containing both ionically cross-linked (with calcium, as represented by red circles) and covalently cross-linked polymers (represented by black and blue lines). Upon crack formation and propagation, a process zone (represented by orange area) is able to dissipate significant amounts of energy as the ionic cross-links break. (b) Use of the TA as a cardiac tissue sealant to prevent leakage as the porcine heart undergoes inflation. (c) Adherence of TA to the liver as it remains bonded while being stretched out to 14 times its initial length (λ). Scale bars, 20 mm. (d) In vivo implementation of TA on blood-exposed surface of beating porcine heart. Adapted with permission.[165] Copyright 2017, Science.