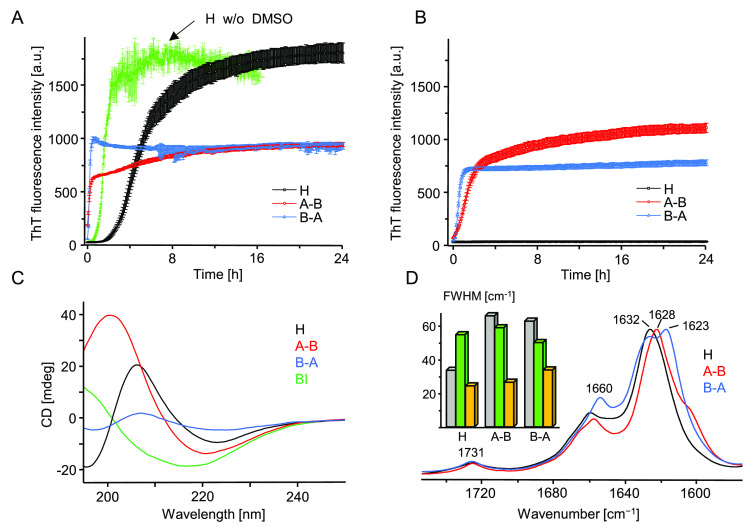
Figure 4.
ThT-fluorescence-monitored kinetics of amyloidogenic reassociation of DMSO-dissolved monomers of H, A–B, and B–A in the presence (A) and absence (B) of 50 mM NaCl. Aggregation was initiated by rapid mixing of concentrated solutions of peptides in 90 vol/vol % DMSO/acidified H2O (24 h + 24 h preincubation protocol) with an excess of acidified aqueous solution. At the start of the experiment reported in (A), each peptide was dissolved at 0.5 mg/mL concentration in 9 vol/vol % DMSO in aqueous 20 μM ThT in 50 mM NaCl, pH 1.9. Sample conditions pertaining to (B) were analogous except that no NaCl was added. The green trajectory in (A) depicts typical kinetics of H-fragment reassociation under similar conditions but with DMSO replaced with approximately 500 mM GdnHCl.31 At the end of the (A) kinetic experiment, amyloid precipitates were collected from the plate and after extensive washing with 50 mM NaCl, pH 1.9, were subjected to far-UV CD (C) and ATR FT-IR (D) measurements. CD spectra were collected at 25 °C for 0.04 mg/mL suspensions of aggregates in acidified H2O (pH 1.9) placed in 10 mm quartz cuvette; a CD spectrum of BI amyloid is overlaid for comparison. The inset histogram in (D) presents full width at half-maximum (fwhm) values of the amide I band collected for crude (gray), DMSO-dissolved (green), and collected at the end of the kinetic experiment (orange) peptides.