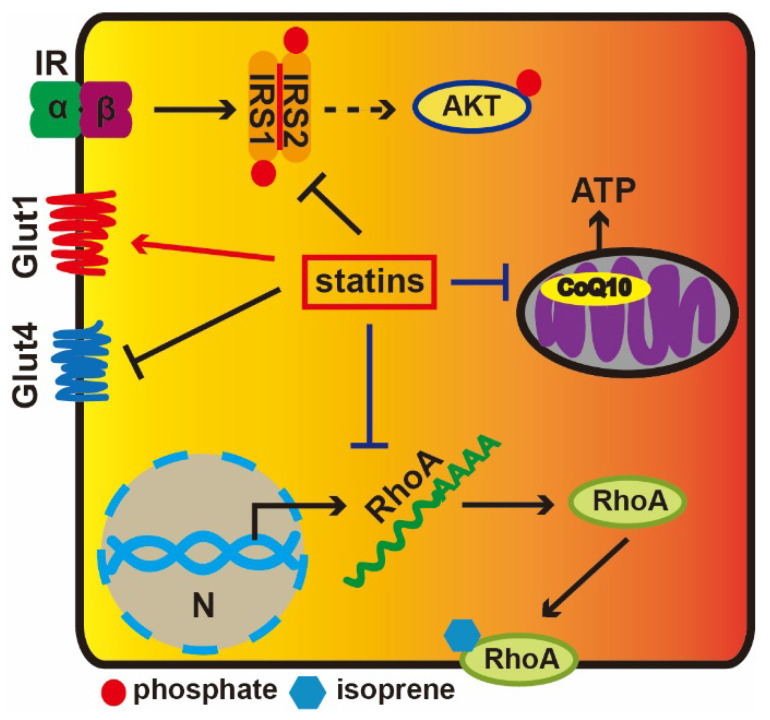
Figure 1.
The diabetogenic mechanisms of statins. Extracellular insulin can activate Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase, which results in the phosphorylation of IRS1, and AKT is subsequently activated. Statins could facilitate GLUT1 transcription, while repress GLUT4. Statins prevent RhoA from transferring to the cell membrane via inhibiting its translation. Statins reduce CoQ10 levels via depressing the HMG-CoA activity to inhibition of the mevalonate pathway impairing mitochondrial electron transport chain and ATP production.