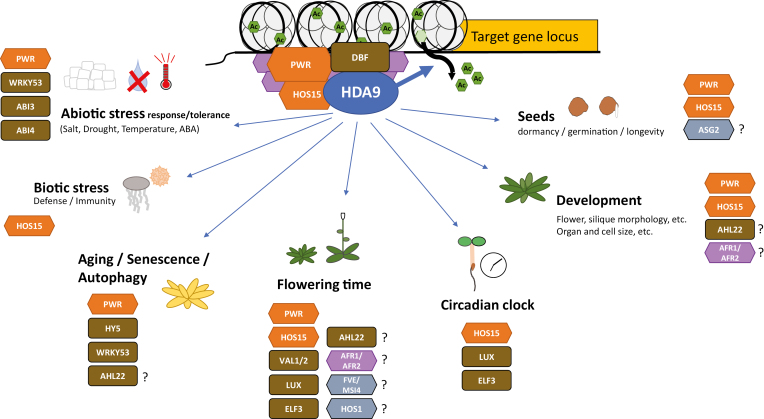
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the HDA9–PWR–HOS15 core histone deacetylase complex and their roles in plant development and responses to the environment. The catalytic HDAC HDA9 (blue oval), together with its core complex components PWR and HOS15 (orange elongated hexagons) and other structural components (purple hexagon), such as AFR1/AFR2, facilitate the de-acetylation (green hexagons) of histones in nucleosome complexes (gray circles), around which two turns of DNA are wrapped (black lines). This affects chromatin accessibility for regulatory proteins and the transcription machinery, and thereby controls the expression of its target genes (yellow box). The HDA9–core histone deacetylase complex is targeted to DNA promoter elements by DNA-binding factors (DBFs; brown boxes), that includes transcription factors such as WRKY53, HY5, ELF3, ABI3, and ABI4. Other known HDA9 partners are the DNA-binding proteins AHL22, VAL1, and VAL2, as well as ASG2, FVE/MSI4, and HOS1 (gray hexagons). The HDA9–PWR–HOS15 complex regulates diverse processes throughout the plant’s life cycle as well as responses and tolerance to the indicated biotic and abiotic stresses. The diverse HDA9-mediated processes and responses rely on different DNA-binding and other proteins (known factors are depicted in association with the mentioned process/response).