Fig. 6.
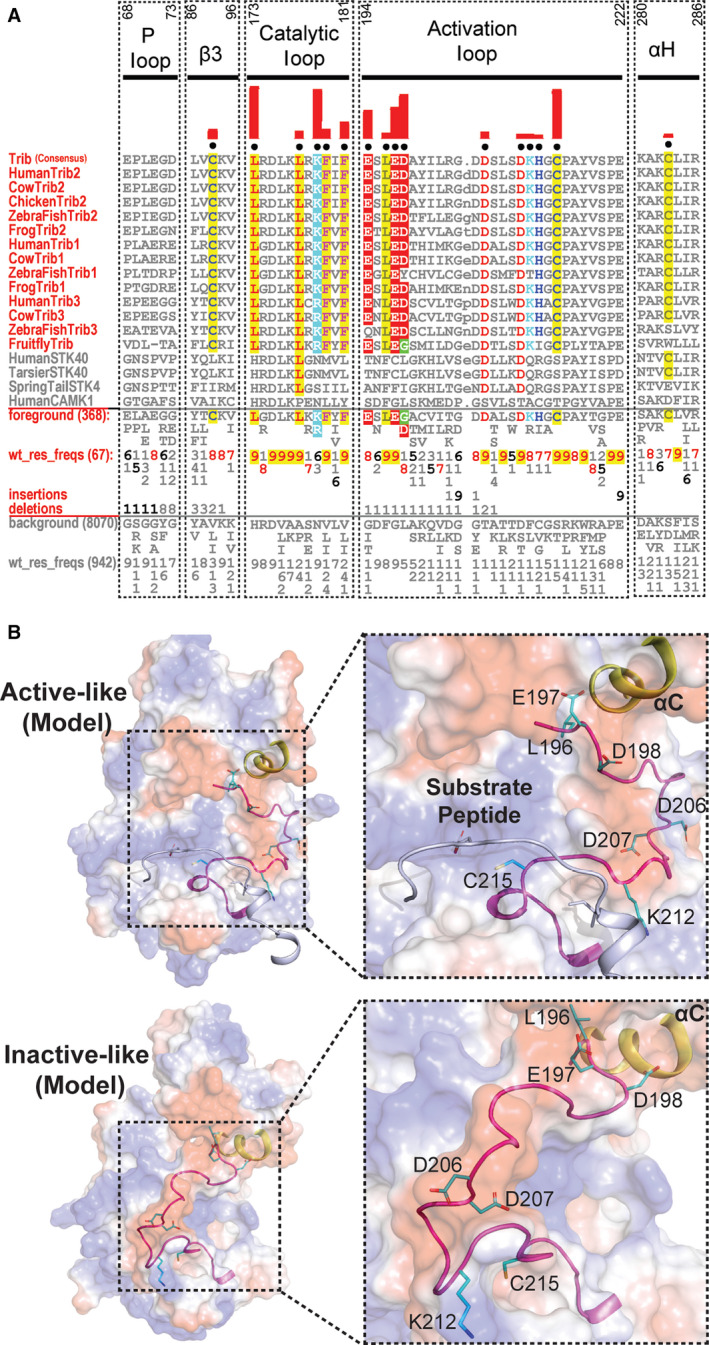
Analysis of unique features of TRIB and STK40 pseudokinases in the activation segment. (A) CHA 31, showing sequence constraints distinguishing TRIB kinases from other closely related CAMKs. Selective TRIB sequences from diverse organisms are shown in the display alignment. Foreground sequences include TRIB pseudokinases, whilst the background includes related CAMK sequences; human canonical CAMK1 is provided for reference. Please refer to Fig. 1 legends for further details. (B) Surface electrostatic of TRIB2 homology models in the ‘active‐like’ (PDB ID: 6DC0) and ‘inactive‐like’ (PDB ID: 5CEM) 57 states. The activation segment of the ‘inactive‐like’ state was not resolved in the crystal structure and was therefore modelled by loop modelling in Rosetta 86, 87. Distinguishing pattern residues in the activation loop are shown as sticks. TRIB‐specific residues are coloured in cyan. The C‐helix is coloured in yellow, and the activation loop is shown in magenta. Substrate peptide in the left panel is shown as a cartoon and coloured in blue/white. UniProt accession numbers for the sequence analysis are as follows: Human TRIB2: Q92519; Cow TRIB2: Q5GLH2; Chicken TRIB2: Q7ZZY2; Zebrafish TRIB2: E7F3S2; Frog TRIB2: Q76D08. Human TRIB1: Q96RU8; Cow TRIB1: A6QLF4; Zebrafish TRIB1: E7FD70; Frog TRIB1: F7BWB1. Human STK40: Q8N2I9; Tarsier STK40: A0A3Q0E403; Springtail STK40: A0A1D2MVE9. Human CAMK1: Q14012.
