FIGURE 1.
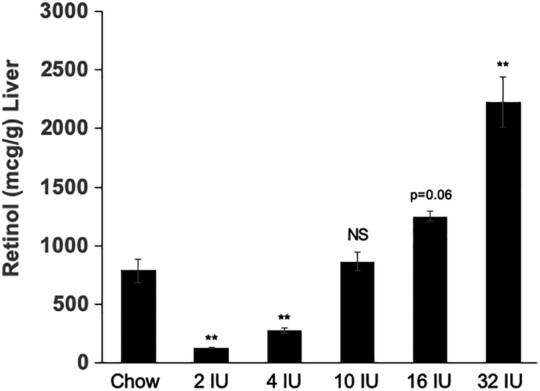
Dose‐dependent changes in maternal liver retinol levels with altered vitamin A content of the maternal diet. Levels of total retinol (mcg/g) were measured in livers from wild type (WT) C57Bl/6 females fed chow or purified diets with defined levels of vitamin A (international units; IU per gram) as retinyl palmitate for 3 months beginning at weaning. There was a dose‐dependent increase in vitamin A status of dams with increasing vitamin A content of the diet. The 10 IU diet resulted in similar liver retinol levels as the chow diet which contains greater than 15 IU vitamin A per gram chow primarily as vitamin A acetate and beta‐carotene. The AIN‐93G control diet contains 4 IU vitamin A per gram diet and resulted in a significant reduction in liver retinol levels as compared to dams fed chow or 10 IU diets. Statistical significance was calculated by ANOVA with post hoc analysis by Tukey’s test comparing all means to the to the chow diet. *p <.05; ** p <.01
