FIGURE 2.
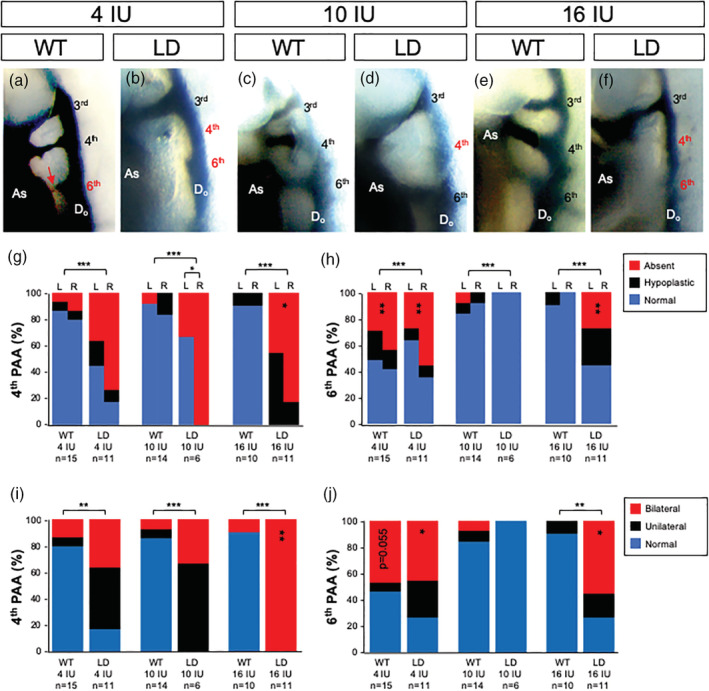
Pharyngeal Arch Artery (PAA) development is altered with changes in vitamin A content of the maternal diet. (a)–(f) Representative right lateral images of E10.5 WT (WT; a, c, e) and LgDel (LD; b, d, f) embryos with PAAs visualized by intercardiac India ink injection. Embryos were from dams fed a purified diet containing 4 IU (a, b), 10 IU (c, d) or 16 IU (e, f) vitamin A as retinol palmitate per gram. The number of embryos (n) analyzed per treatment is indicated. Hypoplasia (red arrow in panel a) or absence of the fourth and sixth PAAs was the feature scored for quantitative phenotypic analysis and indicated by labels in red. The percentage of normal, hypoplastic or absent fourth (g) or sixth (h) PAAs scored on the left (L) or right (R) is shown for each experimental condition. The percentage of unilateral, bilateral or normal defects for the fourth (i) or sixth (j) PAAs is shown. Statistical significance was determined by chi square and shown as *p <.05; **p <.01 or ***p <.0001. Significant differences between genotypes are indicated by brackets over the bars and within genotypes by vertically aligned asterisks within bars. AS, aortic sac; DoA, dorsal aorta
