FIGURE 3.
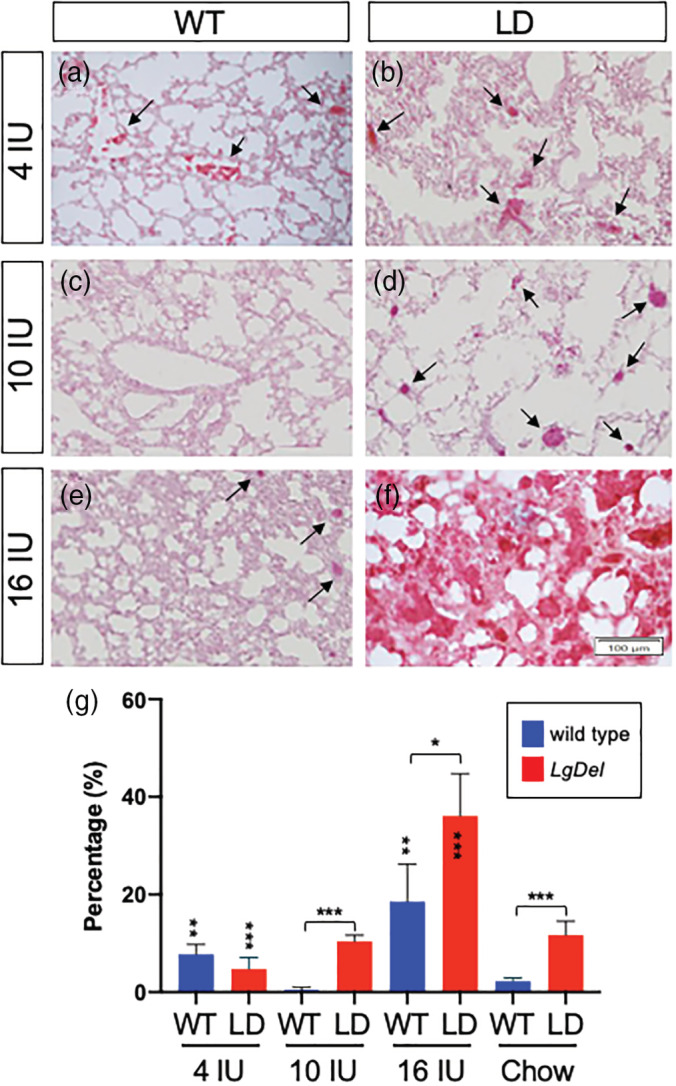
Altering maternal dietary vitamin A intake influences the severity of lung inflammation in the lungs of P7 WT and LgDel pups. (a)–(f). Representative images of H&E stained lungs sections from P7 WT (a, c, e) and LgDel (LD; b, d, f) pups from dams fed a purified diet containing 4 IU (a, b), 10 IU (c, d) or 16 IU (e, f) vitamin A as retinol palmitate per gram. Dark red staining indicates dilation of blood vessels that occurs with lung inflammation (arrows). Note the dramatic increase in inflamed tissue in the lungs of LgDel pups from dams fed the 16 IU diet in panel f. (g) An inflammation ratio was quantified by measuring the area of dark red staining over the total area (see Figure S1 for detailed explanation of method) from five sections averaged from five individuals per group. Statistical significance was determined by ANOVA with a Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. Significant differences between genotypes are indicated by brackets over the bars and within genotypes by vertically aligned asterisks within or above bars. *p <.05; **p <.01; ***p <.0001
