FIGURE 4.
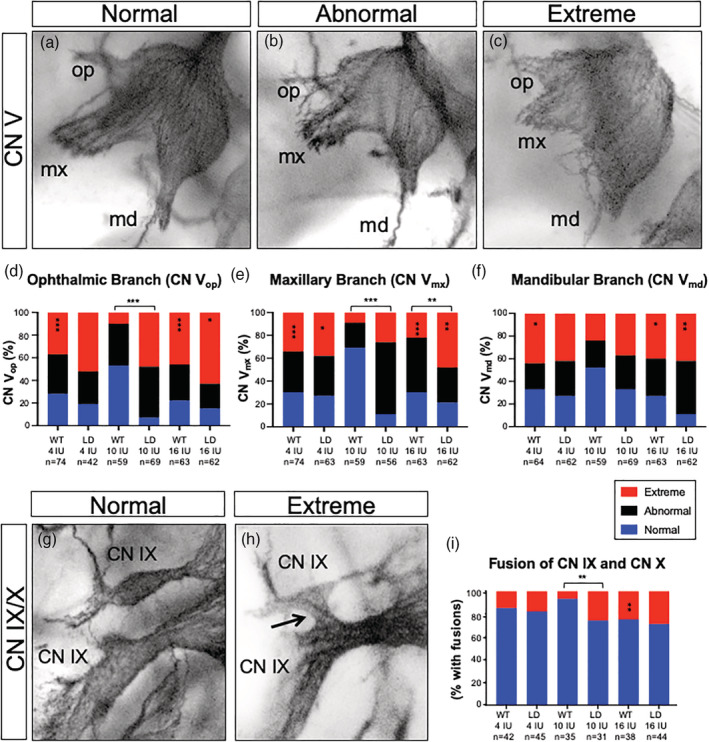
Vitamin A content of the maternal diet alters the incidence and severity of cranial nerve abnormalities in both LgDel embryos and WT littermates. (a)–(c) Representative images showing typical examples of CN V scored as (a) normal, (b) abnormal or (c) extreme. (d)–(f). Quantitation of abnormalities of the ophthalmic (CN Vop, panel d) maxillary (CN Vmx, panel e) and mandibular (CN Vmd, panel f) branches of CN V were scored separately in E10.5 LgDel (LD) embryos and WT littermates from dams fed a purified diet containing 4 IU, 10 IU or 16 IU vitamin A as retinol palmitate per gram. (g, h) Representative images of CN IX/X scored as (g) normal or (h) extreme when fused. (i) Quantitation of CN IX/X fusions. Statistical significance was determined by chi square. *p <.05; **p <.01; ***p <.0001
