Fig. 2.
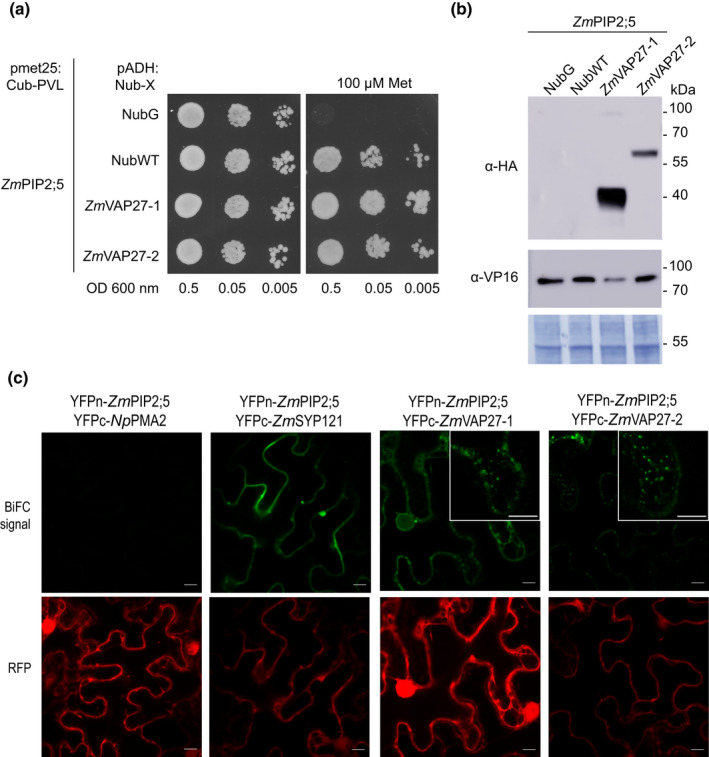
ZmPIP2;5 interacts with ZmVAP27‐1 and ZmVAP27‐2. (a) Spilt‐ubiquitin assay (SUS). Yeast coexpressing the ZmPIP2;5‐Cub‐PLV Met‐repressible bait construct and the prey constructs NubG‐ZmVAP27‐1, NubG‐ZmVAP27‐2, NubG, or NubWT were dropped in a dilution series (OD 0.5, 0.05 and 0.005) onto synthetic medium with or without 100 µM methionine to repress bait expression. Yeast growth was recorded after incubation for 48 h. This experiment was repeated with three independent transformed yeast lines for each construct pair. (b) Immunoblot to verify bait and prey fusion protein expression in yeast used for the SUS. The preys were revealed using anti‐haemaglutinin (anti‐HA) antibody and the bait (ZmPIP2;5) was revealed using an anti‐VP16 antibody. NubG and NubWT do not contain an HA‐tag. The expected molecular weights of the proteins were: NubG‐ZmVAP27‐1, 40 kDa; NubG‐ZmVAP27‐2, 60 kDa, and ZmPIP2;5‐Cub‐PLV, 77 kDa. Polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane Coomassie R250 staining (bottom) was used to control the protein loading. (c) Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) signals for the pairs YFPn‐ZmPIP2;5/YFPc‐NpPMA2 (negative control), YFPn‐ZmPIP2;5/YFPc‐ZmSYP121 (positive control), YFPn‐ZmPIP2;5/YFPc‐ZmVAP27‐1, YFPn‐ZmPIP2;5/YFPc‐ZmVAP27‐2. BiFC signal (YFP) is shown in green, and the RFP signal in red serves as a transfection control. Bars, 10 µm. YFP signal was detected with a bright dot pattern for the YFPn‐ZmPIP2;5/YFPc‐ZmVAP27‐1 and YFPn‐ZmPIP2;5/YFPc‐ZmVAP27‐2 pairs (insets).
