Fig. 7.
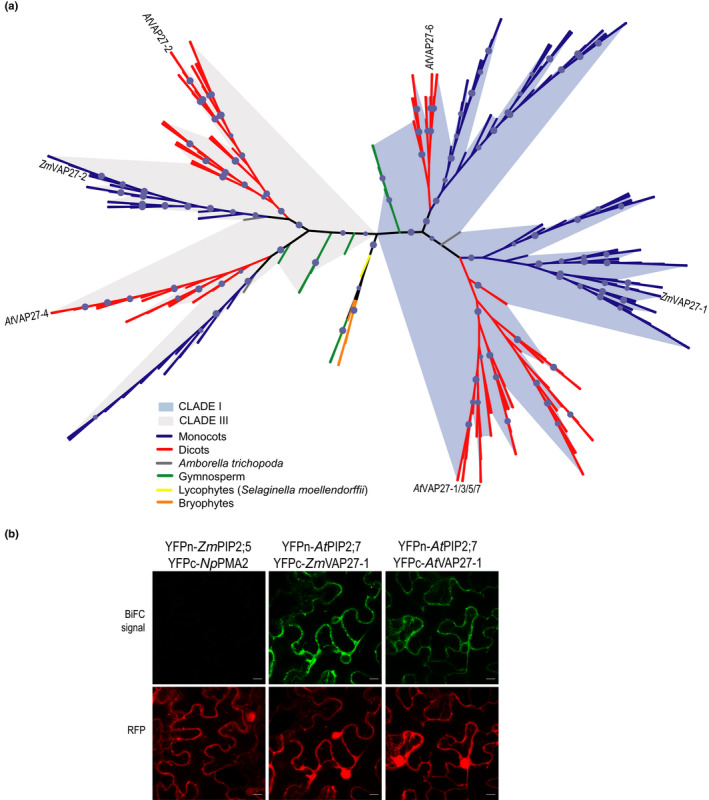
VAP27 protein phylogenetic analysis and conservation of the PIP–VAP27 interaction in Arabidopsis. (a) ZmVAP27‐1 and ZmVAP27‐2 homology group phylogenetic tree reconstructed by maximum likelihood. Branch support was assessed by the ultrafast bootstrap approximation with 1000 replicates (values ≥ 95 are represented by a blue circle). Maize VAP27‐1, VAP27‐2 and Arabidopsis VAP27s are shown in the tree. Branches are coloured according to the taxonomy in the accompanying legends. The shadows emphasise the expansion of two different clades. (b) AtPIP2;7 interacts with the Arabidopsis and maize VAP27‐1 proteins. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) signals for the pairs YFPn‐ZmPIP2;5/YFPc‐NpPMA2 (negative control), YFPn‐AtPIP2;7/YFPc‐ZmVAP27‐1, and YFPn‐AtPIP2;7/YFPc‐AtVAP27‐1. BiFC signal (YFP) is in green, and the RFP signal is in red and serves as a transfection control. Bars, 10 µm.
