FIG 1.
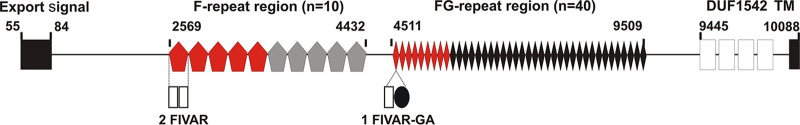
Schematic representation of the Embp architecture. The 1-MDa Embp carries two major repetitive regions consisting of repeats each encompassing 170 and 125 amino acids (aa), respectively. The 170-aa repeat is referred to as F-repeat and is present in 10 copies (indicated by pentagons). The 125-aa repeat, referred to as FG-repeat, can be found in 40 copies (each indicated by a diamond). Previous bioinformatics analysis (22) identified 22 Found in Various Architectures (FIVAR) modules within the F-repeat region (indicated by open boxes). One F-repeat is represented by two FIVAR modules. The FG-repeat region is predicted to contain 38 G-related Albumine binding (GA) modules (indicated by a filled circle), each associated with one FIVAR module. Each FG-repeat represents a pair of GA and FIVAR modules. Experimental evidence demonstrates that the predicted modular architecture does not match the actual structural organization derived from X-ray crystallography (Fig. 5). An N-terminal export signal containing an YSIRK motif, C-terminal domains of unknown function (DUF1542) and a putative transmembrane region (TM) are bioinformatics predictions. Pentagons and diamonds filled red indicate five F-repeats and nine FG-repeats that were fused to the export signal and the putative cell wall binding region for in trans expression in staphylococci. Upper numbers indicate amino acid positions referring to the Embp amino acid sequence.