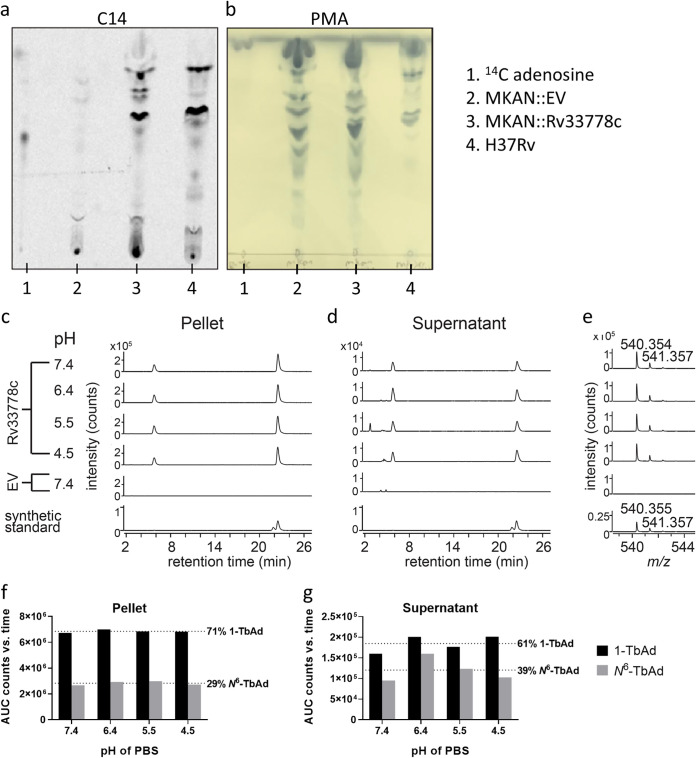
FIG 1.
M. kansasii::Rv3377-78c produces adenosine-linked lipids 1-TbAd and N6-TbAd. (a) Detection of adenosine-linked lipids extracted from M. kansasii::EV (MKAN::EV), M. kansasii::Rv3377-78c (MKAN::Rv33778c), and M. tuberculosis (H37Rv) through radiolabeling and separation using normal-phase silica thin-layer chromatography. (b) Visualization of migration pattern of total lipids from each sample after staining with 5% phosphomolybdic acid reagent. (c to e) Lipids from M. kansasii derived from cell pellets or culture supernatant incubated for 2 h at the indicated pH, neutralized and then extracted with organic solvent. Product was analyzed in comparison with a synthetic standard for 1-TbAd, where the slightly later and larger peak corresponds to native 1-TbAd from M. tuberculosis. (e) The mass spectra of lipids extracted from 21 to 22 min for M. kansasii show an m/z value that matches with the measured and expected mass of a 1-TbAd standard (21). (f and g) Total extracted lipids expressed as area under the curve (AUC) from counts versus retention time of the extracted ion chromatogram. Synthetic 1-TbAd (1.0 μM) was used as the standard.