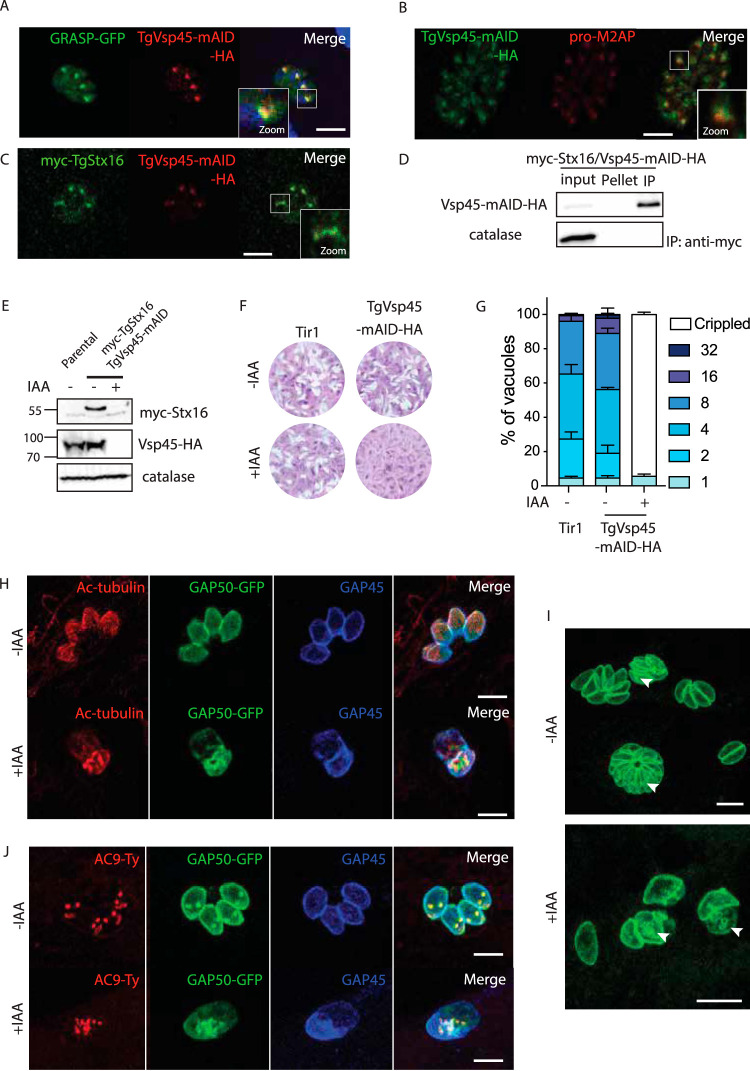
FIG 2.
Vsp45 is implicated in the IMC formation of Toxoplasma gondii (A) C-terminal epitope tagging of TgVsp45 at the endogenous locus partially colocalizes with the Golgi marker GRASP-GFP. (B) C-terminal epitope tagging of Vsp45 at the endogenous locus partially colocalizes with the ELC marker proM2AP. (C) IFA showing the colocalization of the C-terminal tagged Vsp45-HA and N-terminal tagged myc-Stx16. (D) Vsp45-mAID-Ha coimmunoprecipitates with myc-Stx16. (E) Vps45 knockdown leads to a decrease in N-terminal tagged myc-Stx16 protein steady-state levels as shown by the Western blot. Catalase is used as loading control. (F) Plaque assay of TgVps45-mAID-HA and the Tir1 parental strain in the presence or absence of IAA. TgVps45-mAID-HA knockdown but not the parental Tir1 strain displays a severe growth defect in the presence of IAA. (G) TgVps45-mAID-HA knockdown ± IAA. Parasite morphology is grossly affected following depletion of Vps45. Error bars represent the ± SD for three independent experiments. (H) IFA of VspVps45-mAID-HA parasites ± IAA (24 hours). GAP50-GFP and subpellicular microtubules are not formed in the absence of Vps45. GAP50, IMC; GAP45, parasite periphery. (I) IFA of Vsp45-mAID-HA parasites ± IAA (24 hours). Parasites depleted in Vsp45 exhibit an asynchronous block in the IMC formation. GAP50-GFP, IMC marker. (J) IFA of TgVps45-mAID-HA parasites ± IAA (24 hours). Conoid biogenesis is not impaired in Vps45-depleted parasites. Apical cap, AC9-Ty. GAP50, IMC; GAP45, parasite periphery. Scale bars for all IFA = 7 μm.