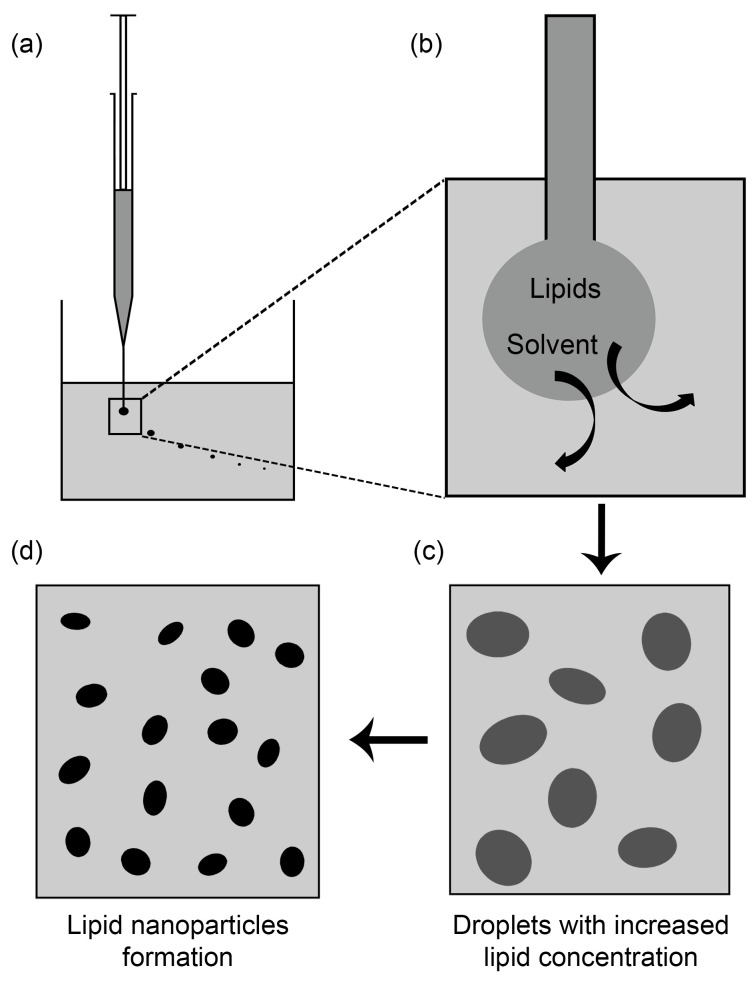
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of lipid-nanoparticle formation using the solvent injection method. Lipids and drugs are dissolved in a water-miscible solvent (organic phase) and injected into an aqueous phase containing emulsifiers (a). Following injection, the solvent gradually diffuses into the aqueous phase (b), which leads to droplet division and a reduction in droplet size while lipid concentration is increased (c). Consequently, solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers are formed and stabilized by the emulsifiers (d).