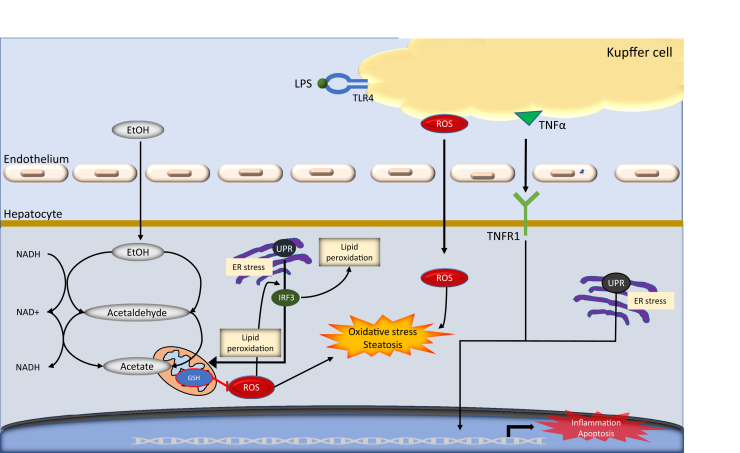
Figure 1.
A schematic of the critical roles of Kupffer cell injury in ethanol metabolism. The oxidation of ethanol to acetate is a two-step process performed by the enzymes alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) that use NAD+ as a cofactor. During the two-step process, the ADH and ALDH reactions allow the accumulation of NADH, reducing the NAD+/NADH ratio in the mitochondria, which initiated the oxidative stress and steatosis process. ER, endoplasmic reticulum; EtOH, ethanol; GSH, glutathione; IRF, interferon regulatory factor; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TLR, toll-like receptor; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; TNFR1, tumor necrosis factor receptor 1; UPR, unfolded protein response.