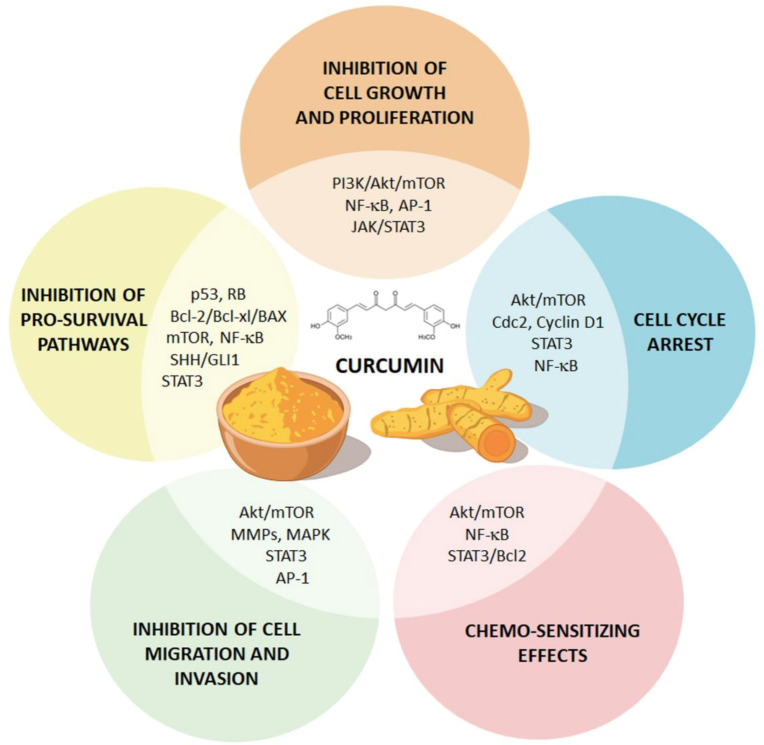
Figure 1.
Curcumin modulates major glioblastoma multiforme (GBM)-associated signaling pathways. The cartoon summarizes the major effects of curcumin on GBM cells. In fact, curcumin was shown to broadly affect core-signaling pathways of GBM neurobiology. For instance, curcumin suppresses tumor growth by inhibiting tumor-promoting pathways (i.e., nuclear factor κB (NF-kB), phosphoinositide 3-kinases/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin (PI3K/Akt/mTOR), Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription (JAK/STAT3) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways), while up-regulating major tumor-suppressing (i.e., p53 and p21, and caspase).