Figure 5.
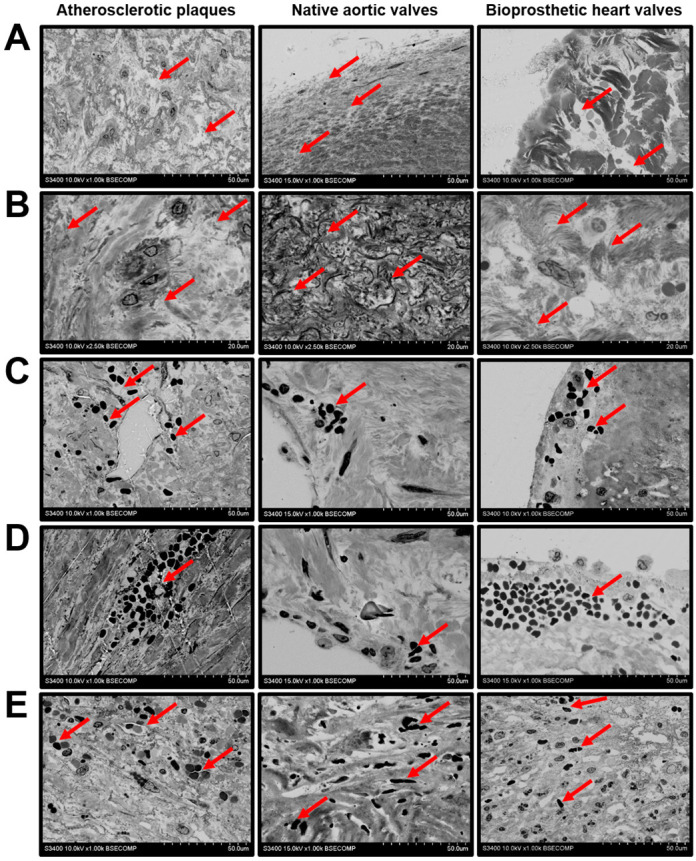
ECM degradation and haemorrhages in atherosclerotic plaques, calcified native AVs, and failed BHVs. (A) Loss of the ECM integrity upon the protease- and fatigue-mediated degradation of the ECM components (indicated by red arrows), magnification 1000×. (B) Loss of the ECM fiber orientation (indicated by red arrows), magnification 2500×. (C) Haemorrhagic infiltration (indicated by red arrows) because of leaky plaque neovessels or the stress-induced penetration of the inflow valve surface, magnification 1000×. (D) Delamination of the neointimal and valvular tissue (indicated by red arrows) upon the accumulation of blood in the cavities formed after the ECM degradation, magnification 1000×. (E) Haemorrhagic infiltration of deep ECM layers (indicated by red arrows) upon the massive intraplaque or intravalvular bleeding, magnification 1000×.
