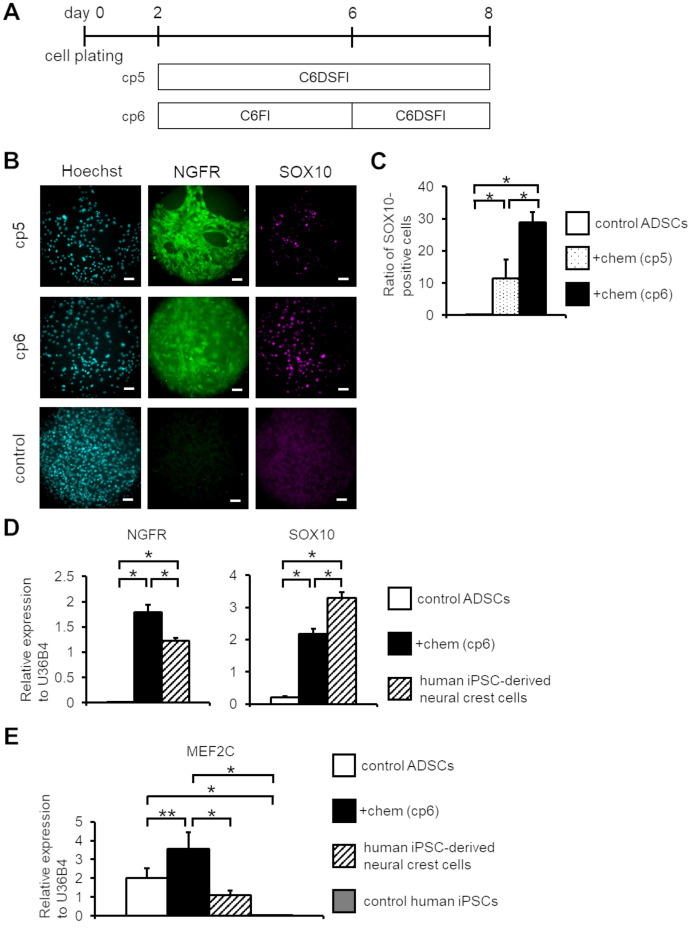
Fig 2. Optimizing chemical induction methods to induce SOX10 expression in human ADSCs.
(A) Schematic of the cell induction methods. Two combinations of small molecular cocktails (cp5, 6) were tested on human ADSCs. (B) Immunofluorescent analysis of NGFR and SOX10 expression in control and chemical-treated human ADSCs. Immunofluorescent analysis was performed on day 8 samples. Scale bar; 100 μm. (C) Ratio of SOX10-positive cells to Hoechst-positive cells in control ADSCs and chemical (the cp5 and cp6 condition)-treated ADSCs at day 8 by immunofluorescent analysis. (n = 4, error bar shows SDs; one-way ANOVA Tukey post-test). (D) qPCR analysis of NGFR and SOX10 expression among control ADSCs, chemical (the cp6 condition)-treated ADSCs on day 8, and human iPSC-derived neural crest cells. The expression values were normalized to that of U36B4. (n = 3, error bar shows SDs; one-way ANOVA Tukey post-test). (E) qPCR analysis of MEF2C in control ADSCs, chemical (the cp6 condition)-treated human ADSCs on day 8, human iPSC-derived neural crest cells, and control human iPSCs. The expression values were normalized to that of U36B4. (n = 3, error bar shows SDs; one-way ANOVA Tukey post-test). C; CHIR, 6; E-616452, F; FSK, D; DM, S; SB, and I; ISX9. *P < 0.01, **P < 0.05.