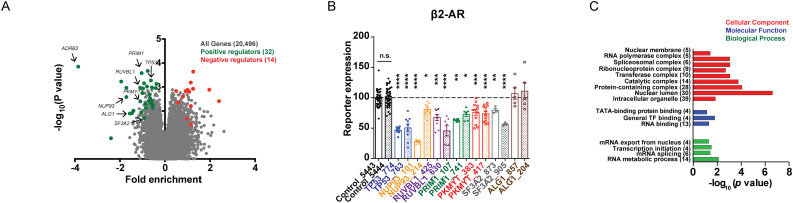
Fig 3. A high-throughput CRISPR-based genomic screen identifies novel modulators of GPCR signaling.
(A) Volcano plot of gene enrichment in the “high” versus “low” fractions from all seven CRISPRi libraries. Significant hits with “hit strength” FDR ≤ 10% are color-coded based on their phenotype, and genes selected for follow-up validation are indicated with arrows. (B) Validation of the functional effects on β2-AR-dependent CRE-GFP reporter upregulation for a subset of novel regulators identified by the CRISPRi screen. Two sgRNAs per gene were selected based on screen phenotype, individually cloned and tested in batches. Cells were treated with 1 μM Shield-1 and 1 μM isoproterenol for 4 h and analyzed by flow cytometry. Mean GFP signal of the two control sgRNAs (5443 and 5444) for each batch was set to 100% and used to normalize the mean GFP values for all sgRNAs from that batch, as described in the “Materials and Methods” section. Data shown are mean from n = 3–12 per gene-specific sgRNA, and n = 41–42 for NTCs. (C) Enriched Gene Ontology categories (S5 Table) among High-confidence hits identified through “high”/”low” comparison. Error bars = ± s.e.m. **** = p ≤ 0.0001; *** = p ≤ 0.001; ** = p ≤ 0.01; * = p ≤ 0.05 by one-way ANOVA test.