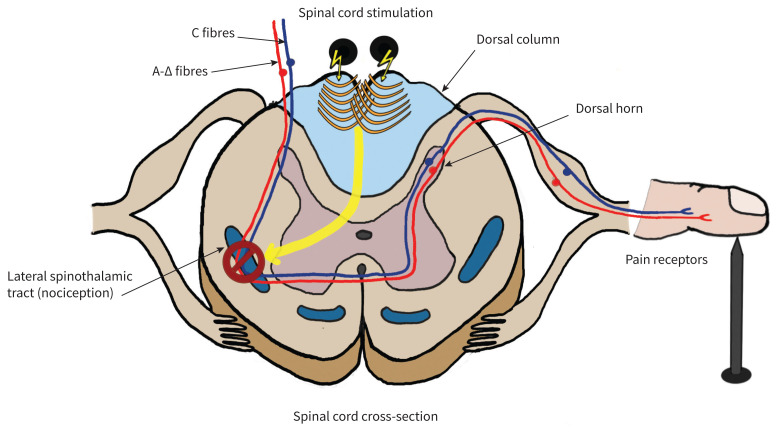
Figure 1:
Gate theory of pain. This theory postulates that pain signal transmission via the spinothalamic tract from pain-transmitting fibres (unmyelinated C fibres and lightly myelinated A-Δ fibres) is blocked by stimulating the dorsal column large myelinated fibers and the polysynaptic interneurons (PSINs). The PSINs then fire back up on the dorsal horn, blocking pain receptors from synapsing. Illustration by Jean Chan.