Figure 1.
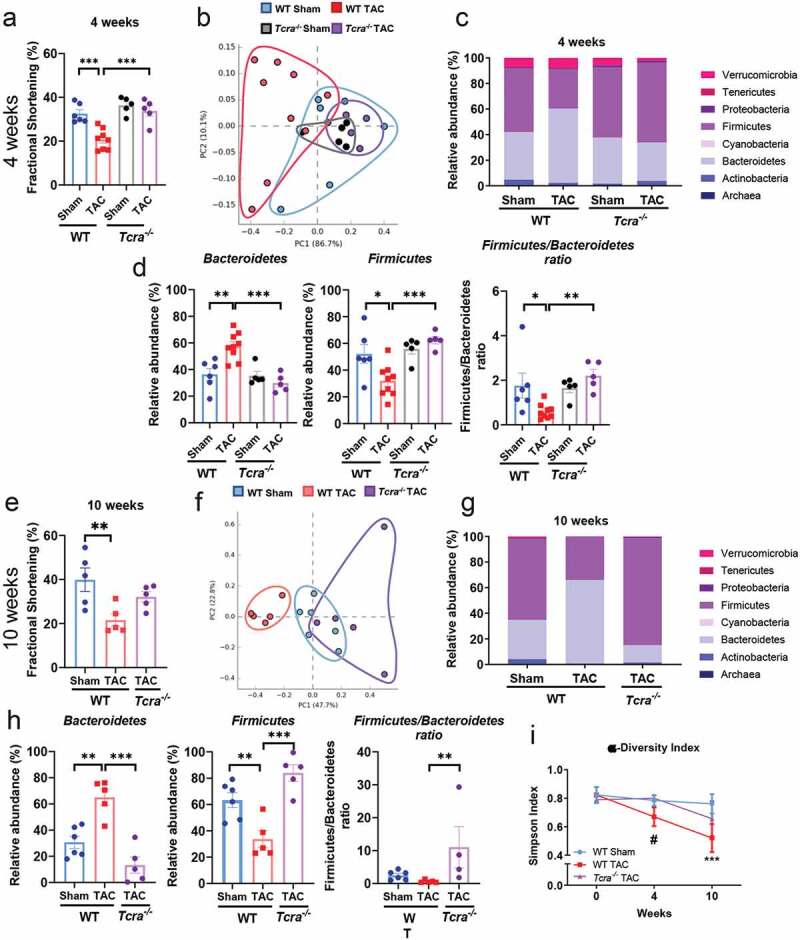
Cardiac pressure overload induces gut dysbiosis characterized by a low Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio in WT but not in Tcra−/- mice. Wild type (WT) and Tcra−/- mice were subjected to 4 weeks (a-d, i) or 10 weeks (e-i) Sham or TAC surgery and echocardiography was performed at 4 weeks (a) and 10 weeks post-surgery (e). Principal component analysis (PCA) clustering of gut microbial populations generated after 16S rRNA sequencing of fecal pellets of WT and Tcra−/- at 4 weeks (b) and 10 weeks (f) post-Sham or TAC surgery. Each point represents one mouse. Relative abundance of main phyla of gut microbiota in fecal pellets (c, g), and specifically Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes and Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio (d, h), from WT and Tcra−/- mice harvested at 4 weeks (c, d) and 10 weeks post-Sham or TAC (g, h). Alpha diversity representation over time in WT and Tcra−/- mice (i). *p < .05; **p < .01; ***p < .001; ns = non statistically significant. Statistical analysis: ANOVA test with a Tukey-Kramer posthoc test (a-j), and 2-way ANOVA test and Tukey’s multiple comparison test were used (I). #p < .05 WT TAC vs Tcra−/- TAC; ***p < .001 WT Sham vs WT TAC (I)
