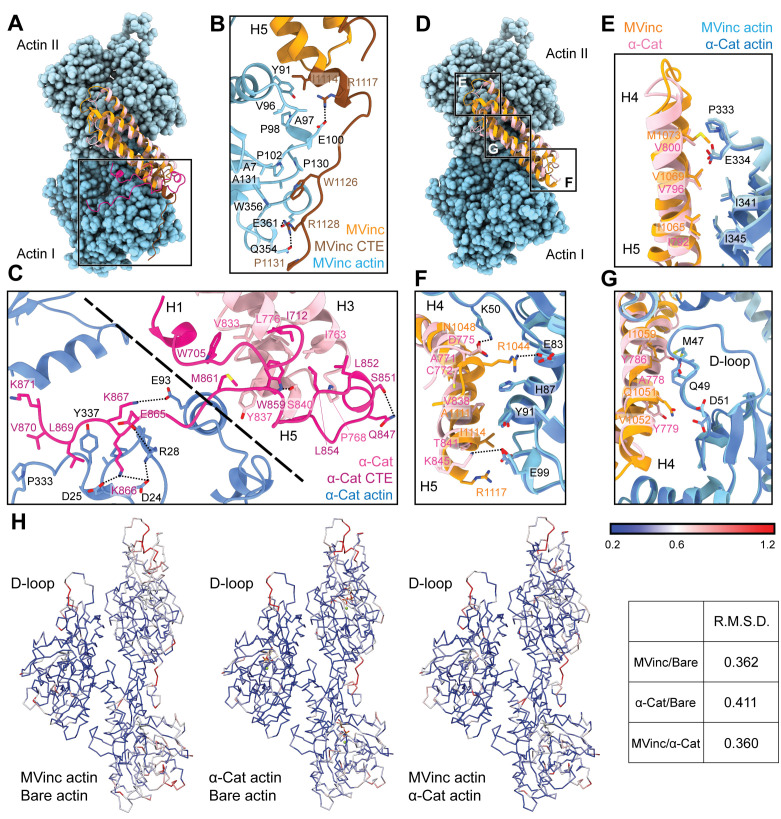
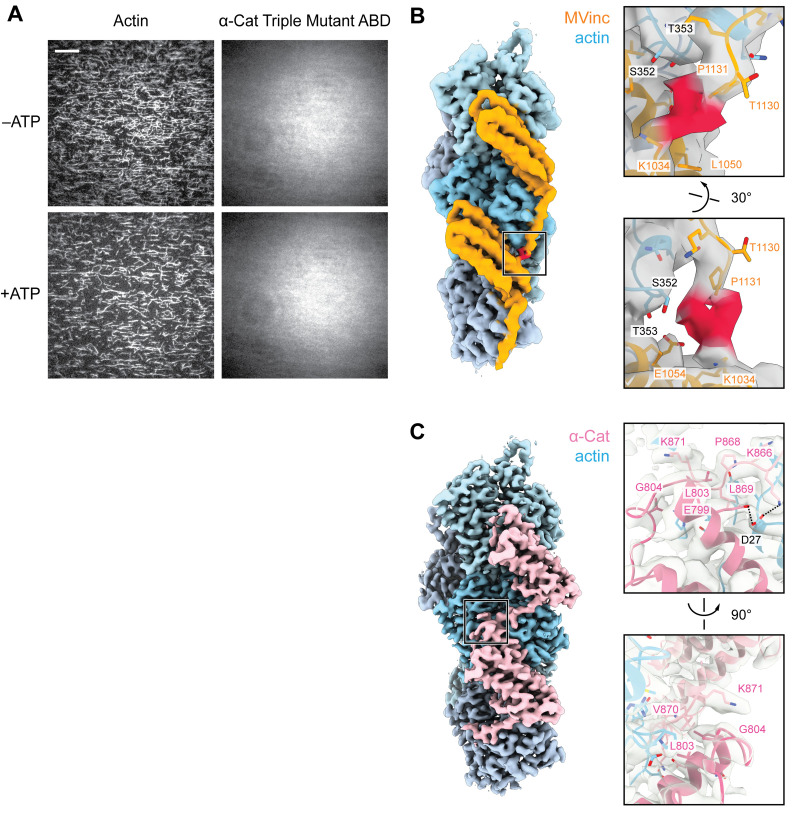
Figure 5. The actin-binding interfaces of metavinculin and α-catenin.
(A) Overlay of the metavinculin ABD-actin complex and α-catenin ABD-actin complex atomic models highlighting C-terminal extensions (CTEs) of metavinculin ABD and α-catenin ABD, superimposed on Actin I and colored as in Figure 4. Actins from α-catenin structure are displayed. (B and C) Detailed views of key contacts at minor interfaces: metavinculin CTE and actin (B); within the α-catenin tryptophan latch (right) and between its CTE and actin (left) (C). (D) Overlay of the metavinculin ABD-actin complex and α-catenin ABD-actin complex atomic models highlighting helical binding interfaces of metavinculin ABD and α-catenin ABD, superimposed and colored as in (A). Actins from α-catenin structure are displayed. (E, F, and G) Detailed views of key contacts at the major interface between metavinculin/α-catenin helices H4–H5 and Actin I (E); Actin II (F); Actin II D-loop (G). (H) Actin Cα traces colored by per-residue RMSD from the indicated comparisons. For superposition, segmented actin density from the cryo-EM maps was first aligned, followed by fitting the atomic models into their corresponding maps.