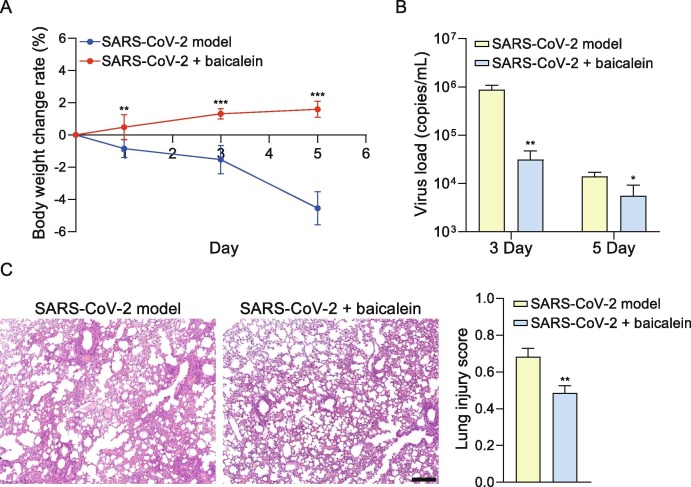
Fig. 3.
Baicalein inhibited the loss of the body weight, reduced virus load and relieved lung injury in mice infected with SARS-CoV-2. (A) The average body weight change rate of mice in model and baicalein groups. Compared with the model group, the average body weight of mice in the baicalein group was significantly increased on the 1st (n = 6), 3rd (n = 6), and 5th (n = 3) day (P < 0.01, P < 0.001 and P < 0.001). Statistical significance was assessed using two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple comparisons test. (B) Baicalein significantly inhibited the virus load of the lung tissue on the 3rd and 5th days after infection (**P < 0.01 and *P < 0.05). Statistical significance was assessed using unpaired t test. (C) The baicalein relieved inflammatory cell infiltration of lung tissue caused by SARS-CoV-2, according to the results of H & E staining. Statistical significance of lung injury score was assessed using unpaired t test. The values are presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.01 vs. SARS-CoV-2 infection model group (scale bar = 250 μm).